
What is rehabilitation and who needs it?
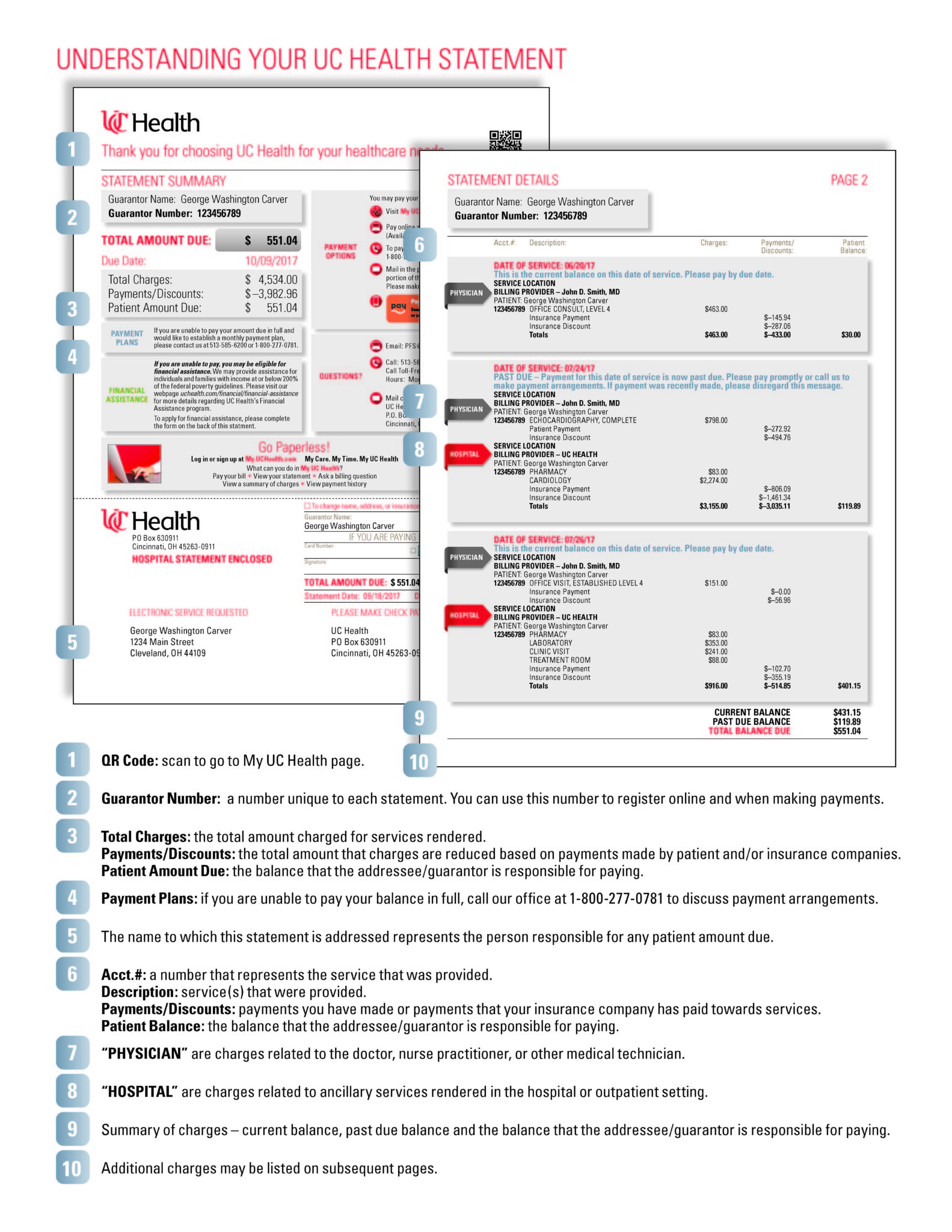
Apr 04, 2022 · Ambulatory. Discharge. Español. Total hip replacement (THR) is surgery to replace a hip joint damaged by wear, injury, or osteoarthritis. It is normal to have increased stiffness and pain after surgery. Your pain and stiffness should get better with exercise. You may be able to go home shortly after surgery.
What can you say to someone in rehab?
May 24, 2017 · Sometimes the most encouraging words for someone in rehab can be simple phrases like “we miss you”, “we are here for you”, and “we love you no matter what.”. Vocalizing our love and support for one another is important regardless of situation, but during recovery from drugs and alcohol, it can be the difference between a recovery ...
Can rehabilitation be personalized for individuals?
Nov 10, 2021 · Rehabilitation can reduce the impact of a broad range of health conditions, including diseases (acute or chronic), illnesses or injuries. It can also complement other health interventions, such as medical and surgical interventions, helping to achieve the best outcome possible. For example, rehabilitation can help to reduce, manage or prevent ...
How do I find a rehab program for someone I care about?
Oct 11, 2021 · To find a rehab program for someone you care about, call our helpline at 1-800-429-7690. We can help them get back on track with their recovery. Relapsing on opioids like heroin or prescription painkillers can be deadly due to your loved one’s reduced tolerance.

What to Say to Someone in Drug Rehab: Encouraging Words for Someone in Rehab
When someone you love is admitted into rehab, people commonly feel helpless and lost. This is usually because they want to help in one way or another, but it’s rare that people know what to say to someone in drug rehab.
Support their Decision to Get Help
When you’re going through drug addiction treatment, you can experience a roller coaster of different emotions. This has a lot to do with the fact that your body is still adjusting to the change in chemical makeup and the new, unfamiliar surroundings.
Stop Enabling Their Drug Use
Once your friend or family member has progressed further into their recovery, they are going to start thinking about life after rehab. Once they start getting their bearings, it’s important to start laying the ground rules for their return.
Remind Them You Care
During inpatient rehabilitation, it’s very easy for patients to feel somewhat isolated from their friends and family on the outside. When you couple this very common response to being cut off from your support, with the depression commonly associated with withdrawals, you end up with a person in need of support and understanding.
Show Them You Empathize With and Understand Them
One of the reasons why knowing what to say to someone in drug treatment can be so hard at times, is because the vast majority of people have no experience with substance abuse treatment and recovery.
What are the challenges of rehabilitation?
Global rehabilitation needs continue to be unmet due to multiple factors, including: 1 Lack of prioritization, funding, policies and plans for rehabilitation at a national level. 2 Lack of available rehabilitation services outside urban areas, and long waiting times. 3 High out-of-pocket expenses and non-existent or inadequate means of funding. 4 Lack of trained rehabilitation professionals, with less than 10 skilled practitioners per 1 million population in many low- and middle-income settings. 5 Lack of resources, including assistive technology, equipment and consumables. 6 The need for more research and data on rehabilitation. 7 Ineffective and under-utilized referral pathways to rehabilitation.
What is the rehabilitation workforce?
The rehabilitation workforce is made up of different health professionals, including physiotherapists, occupational therapists, speech and language therapists, orthotists and prosthetists, and physical medicine and rehabilitation doctors.
How many people in the world do not receive rehabilitation services?
More than half of people living in some low- and middle-income countries who require rehabilitation services do not receive them. The COVID-19 pandemic has led to a new increase in rehabilitation needs as well as causing severe disruption to existing rehabilitation services in 60-70% of countries worldwide.
What percentage of people do not receive rehabilitation services?
Currently, the need for rehabilitation is largely unmet. In some low- and middle-income countries, more than 50% of people do not receive the rehabilitation services they require.
How does rehabilitation help?
It can help to avoid costly hospitalization, reduce hospital length of stay , and prevent re-admissions . Rehabilitation also enables individuals to participate in education and gainful employment, remain independent at home, and minimize the need for financial or caregiver support.
Why is rehabilitation important?
Rehabilitation is an essential part of universal health coverage along with promotion of good health, prevention of disease, treatment and palliative care . Rehabilitation helps a child, adult or older person to be as independent as possible in everyday activities and enables participation in education, work, recreation and meaningful life roles ...
What is the role of splinting after leg amputation?
Positioning and splinting techniques to assist with skin healing, reduce swelling, and to regain movement after burn surgery. Prescribing medicine to reduce muscle stiffness for a child with cerebral palsy.
How many people have OA?
Osteoarthritis (OA) is a leading cause of joint disability in the United States. Approximately 54 million people (23% of adults) have OA, and, of these, 24 million are limited in their daily activities due to OA. 1 Total joint replacement (TJR)—total knee arthroplasty (TKA) and total hip arthroplasty ...
What is peer review in EPC?
Peer reviewers are invited to provide written comments on the draft report based on their clinical, content, or methodological expertise. The EPC considers all peer review comments on the draft report in preparation of the final report. Peer reviewers do not participate in writing or editing of the final report or other products. The final report does not necessarily represent the views of individual reviewers. The EPC will complete a disposition of all peer review comments. The disposition of comments for systematic reviews and technical briefs will be published three months after the publication of the evidence report.
What is technical expert?
Technical Experts constitute a multi-disciplinary group of clinical, content, and methodological experts who provide input in defining populations, interventions, comparisons, or outcomes and identify particular studies or databases to search. The Technical Expert Panel (TEP) is selected to provide broad expertise and perspectives specific to the topic under development. Divergent and conflicting opinions are common and perceived as healthy scientific discourse that fosters a thoughtful, relevant systematic review. Therefore, study questions, design, and methodological approaches do not necessarily represent the views of individual technical and content experts. Technical Experts provide information to the EPC to identify literature search strategies and suggest approaches to specific issues, as requested by the EPC. Technical Experts do not do analysis of any kind; neither do they contribute to the writing of the report. They do not review the report, except as given the opportunity to do so through the peer or public review mechanism.
What is adjunctive modalities?
Adjunctive modalities are either passively applied to patients and/or do not (on their own) have the direct goals of reducing impairments or improving movement-related function, but are used to help other modalities achieve these goals.
What is a movement-related physical goal?
Any movement-related physical goal including improvements beyond the basal (or baseline) state in: mobility and stability of joint function (including flexibility and range of motion), movement control, power and tone of muscles (including strength), gait, endurance; along with the related goal of reducing pain.
What is P rehabilitation?
Another important aspect of (p)rehabilitation is the setting in which it may be delivered. These vary widely, and examples include the acute hospital setting (i.e., immediately postoperative), a skilled nursing facility, outpatient rehabilitation facility, the patient’s home, or a local community center or gym.
How much must an EPC team disclose?
EPC core team members must disclose any financial conflicts of interest greater than $1,000 and any other relevant business or professional conflicts of interest. Related financial conflicts of interest that cumulatively total greater than $1,000 will usually disqualify EPC core team investigators.
Why do addicts fear others?
Addicts often fear that others will lose respect for them, or see them as weak or at fault for their drug use. This concern is compounded when the addiction has progressed to the point that the individual has broken promises, stolen, or otherwise harmed their loved ones.
How long do addiction symptoms last?
Depending on the severity of the addiction, some of these symptoms can linger for weeks or even months. Enduring the discomfort and disturbing moods that come with these symptoms can be discouraging and frightening, even when patients are told what to expect ahead of time.
I. Background and Objectives For The Systematic Review
- Osteoarthritis (OA) is a leading cause of joint disability in the United States. Approximately 54 million people (23% of adults) have OA, and, of these, 24 million are limited in their daily activities due to OA.1 Total joint replacement (TJR)—total knee arthroplasty (TKA) and total hip arthroplasty (THA)—has been one of the most successful therapi...
II. Key Questions
- KQ 1: What are the effects, comparative effects, and harms of (preoperative) prehabilitation services (and specific modalities) for patients with osteoarthritis undergoing elective, unilateral, tot...
- KQ 2: What are the effects, comparative effects, and harms of (postoperative)rehabilitation services (and specific modalities) for patients with osteoarthritis undergoing elective, unilate…
- KQ 1: What are the effects, comparative effects, and harms of (preoperative) prehabilitation services (and specific modalities) for patients with osteoarthritis undergoing elective, unilateral, tot...
- KQ 2: What are the effects, comparative effects, and harms of (postoperative)rehabilitation services (and specific modalities) for patients with osteoarthritis undergoing elective, unilateral, tota...
- KQ 3: What are the effects, comparative effects, and harms of (preoperative) prehabilitation services (and specific modalities) for patients with osteoarthritis undergoing elective, unilateral,tota...
- KQ 4: What are the effects, comparative effects, and harms of (postoperative) rehabilitation s…
III. Analytic Framework
- Figure. Analytic Framework for KQs 1-4: Different types of prehabilitation or rehabilitation for kn…
*denotes important/priority outcomes that will be included in Strength of Evidence tables Abbreviations:KQ = Key Question; MUA = manipulation under anesthesia
IV. Methods
- For all KQs, the systematic review will follow Evidence-based Practice Center (EPC) Program methodology, as laid out in its Methods Guide,39particularly as pertain to reviews of comparative effectiveness and complex meta-analyses. As described below, the Contextual Questions will be addressed using a nonsystematic approach.
v. References
- National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion (NCCDPHP). Arthritis. Atlanta, GA: National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion; 2019. Accessed on June 16...
- Ethgen O, Bruyère O, Richy F, et al. Health-related quality of life in total hip and total knee arthroplasty. A qualitative and systematic review of the literature. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 200…
- National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion (NCCDPHP). Arthritis. Atlanta, GA: National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion; 2019. Accessed on June 16...
- Ethgen O, Bruyère O, Richy F, et al. Health-related quality of life in total hip and total knee arthroplasty. A qualitative and systematic review of the literature. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2004 May;8...
- Rissanen P, Aro S, Slätis P, et al. Health and quality of life before and after hip or knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 1995 Apr;10(2):169-75. doi: 10.1016/s0883-5403(05)80123-8. PMID: 7798097.
- March LM, Cross MJ, Lapsley H, et al. Outcomes after hip or knee replacement surgery for os…
VI. Abbreviations
- AHRQ = Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality AAOS = American Academy of Orthopedic Surgeons APTA = American Physical Therapy Association BMI = body mass index COI = conflicts of interest CMS = Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services CPG = clinical practice guideline CPM = continuous passive motion DALY = disability-adjusted life year ERAS = Enhanced recovery afte…
VII. Summary of Protocol Amendments
- Following the posting of the protocol, the protocol was amended to reflect changes to the proposed taxonomy to be used to code the rehabilitation intervention and language used to describe the components of the intervention (as distinct from adjunctive modalities). Table 1 provides the date, description and rationale for each amendment.
VIII. Review of Key Questions
- AHRQ posted the KQs on the AHRQ Effective Health Care Website for public comment. The Evidence-based Practice Center (EPC) refined and finalized them after reviewing of the public comments and seeking input from KIs. This input is intended to ensure that the KQs are specific and relevant.
IX. Key Informants
- We included a panel of KIs during Topic Refinement. KIs are end users of research, including patients and caregivers, practicing clinicians, relevant professional and consumer organizations, purchasers of health care, and others with experience in making health care decisions. Within the EPC program, the KIs’ role is to provide input into identifying and refining the Key Questions for r…
X. Technical Experts
- Technical Experts constitute a multi-disciplinary group of clinical, content, and methodological experts who provide input in defining populations, interventions, comparisons, or outcomes and identify particular studies or databases to search. The Technical Expert Panel (TEP) is selected to provide broad expertise and perspectives specific to the topic under development. Divergent an…