Cardiac Rehabilitation: Weight and Resistance Training Topic Overview Resistance training with weights, elastic bands, or your own body weight may help you regain the physical strength and confidence to do the daily tasks you performed before your heart problem or surgery.
Why is resistance training important in cardiac rehabilitation?
As patients with myocardial ischaemia and/or poor left ventricular function may develop wall motion disturbances and/or severe ventricular arrhythmias during resistance exercise, the following criteria are suggested for resistance training: moderate-to-good LV function, good cardiac performance capacity [>5-6 metabolic equivalents of oxygen consumption …
What is cardiac rehabilitation?
3 rows · RESISTANCE TRAINING IMPROVES PATIENTS' QUALITY OF LIFE. An aerobic training program is ...
Is resilience training safe for cardiac rehabilitation?
What is Resistance Training? • Resistance training includes activites performed to improve your muscle strength and endurance • It is commonly done with weighted machine and hand weights • You can also use objects around your house, resistance bands, or your own body weight to achieve the same goal
Is resistance exercise harmful to cardiac patients?
Feb 22, 2000 · Recently, the application of resistance testing or training in the rehabilitation of patients with coronary disease in 12 different studies was reviewed. 27 Resistance or circuit weight training was typically added to the physical-conditioning regimens of men with coronary disease who had already been aerobically trained, generally for 3 months or more. The latter …

What are examples of resistance training?
Examples of resistance trainingFree weights – classic strength training tools such as dumbbells, barbells and kettlebells.Medicine balls or sand bags – weighted balls or bags.Weight machines – devices that have adjustable seats with handles attached either to weights or hydraulics.More items...
What does resistance training do to the heart?
Reduces the risk of heart attack or stroke Because strength training increases lean muscle mass, it gives your cardiovascular system places to send the blood being pumped. This results in less pressure on your arteries, which helps reduce the chances of heart-related problems.
What is the meaning of resistance training?
Resistance training is any exercise that causes the muscles to contract against an external resistance with the expectation of increases in strength, power, hypertrophy, and/or endurance.
How is resistance training useful for rehabilitation and rehabilitation?
Results Evidence suggests that RT can increase muscle strength, reduce pain and improve functional ability in patients suffering from CLBP, knee osteoarthritis, and chronic tendinopathy and those under recovery after hip replacement surgery.
What are the disadvantages of resistance training?
Disadvantages:angle specific.limited use in sports.limited strength and endurance gains.cannot monitor intensity.large increases in blood pressure.
Should I do more strength training or cardio?
A cardio workout burns more calories than a weight-training workout. However, your metabolism may stay elevated for longer after weights than cardio, and weight lifting is better for building muscle. Thus, the ideal exercise program for improving body composition and health includes cardio and weights.Oct 24, 2017
What are the 3 types of resistance training?
There are three main types of progressive resistance exercise: isotonic, isokinetic, and isometric exercise. In isotonic exercise, a muscle group is put through a full range of motion via the use of an external load with the speed throughout the range of motion constantly changing.Nov 30, 2021
Is walking considered resistance training?
Walking, home-based weight-bearing resistance training, and its combinations are considered simple, easy, and practical exercise interventions for older adults.Nov 19, 2018
How long is resistance training?
If you're strength training only one day per week, aim for a 60- to 90-minute session; those who train two or three days a week should try for 45- to 60-minute sessions; and 20- to 60-minute sessions for people who train four or five days a week. In general, expect your strength workouts to span 20 to 90 minutes.Sep 8, 2021
Why is strength training important for rehabilitation?
During recovery, building and strengthening the structures e.g. ligaments, tendons and muscles around previously damaged or injured joints literally helps support and take load and pressure off the joint itself. This in turn will reduce pain and discomfort whilst helping build the affected area back to full function.
What is strength training explain briefly about various types of strength training?
The principles of strength training involve manipulation of the number of repetitions (reps), sets, tempo, exercises and force to overload a group of muscles and produce the desired change in strength, endurance, size or shape.
What are precautions of strength training?
Safety tips for resistance trainingProper technique is essential. ... Start slowly. ... Only use safe and well-maintained equipment. ... Don't hold your breath. ... Control the weights at all times. ... Maintain a strong form while lifting, as this will prevent injury through incorrect technique. ... Use the full range of motion.More items...
Why is resistance training important?
Following the proper time-course, safety considerations, and programming guidelines will ensure resistance training helps maximize recovery from a cardiac event and improve quality of life.
What is RT after cardiac rehab?
The RT program design for the patient after cardiac rehabilitation will depend on where the patient plans on exercising upon completion of their allotted cardiac rehabilitation sessions and what RT equipment ( e.g., variable dynamic resistance machines, free weights, and variable resistance [or color] bands/tubing) an individual will have access to. In an ideal situation, upon completion of the monitored phase of cardiac rehabilitation (often referred to as phase II), an individual will be offered the opportunity to continue exercising in the same facility as a member of their maintenance program (often referred to as phases III to IV). Remaining in a familiar environment will increase both an individual's comfort and confidence level in moving forward with their exercise program, particularly RT. However, as is often the case, many patients must find a new place to exercise with different equipment and, just as important, a new staff.
How much weight can a cardiac patient lift?
Cardiac patients were (and sometimes still are) told not to lift anything heavier than 5 to 10 lbs for an indefinite time period after a cardiac event or procedure ( 11 ). This, if anything, will encourage less physical activity ( 1,11 ).
What are the conditions that should be considered when developing an RT program?
Many cardiac patients have other cardiac- ( e.g., hypertension, diabetes, implantable cardiac defibrillators [ICDs], and pacemakers) and noncardiac-related ( e.g., osteoarthritis, osteoporosis, and shoulder impingement) conditions that should be considered when developing an RT program.
What is the benefit of RT?
The benefits of RT for persons with cardiovascular disease are numerous. The most well-known benefit of RT is increased muscular strength and endurance ( 1,4-10 ). Overall muscle strength improvements of 25% to 30% are typically seen ( 4,8-10 ).
Is resistance training safe for cardiac rehabilitation?
Resistance training is safe for selected cardiac rehabilita tion patients and provides a number of health and fitness benefits. It is important for each cardiac patient to follow the proper time course for initiating RT and adhere to specific RT programming and safety guidelines. Cardiac patients should have their RT program adapted to their specific needs and abilities. This will allow them to achieve the benefits of RT, while minimizing the risk of adverse events or injury. Resistance training, like cardiorespiratory exercise, should be continued after the completion of a cardiac rehabilitation program to maintain or further enhance muscular fitness.
Is cardiorespiratory exercise considered a component of cardiac rehabilitation?
Cardiorespiratory exercise has traditionally been the emphasis of cardiac rehabilitation programs. However, resistance training (RT) has gradually become a critical component of cardiac rehabilitation because of its significant health benefits and positive effects on cardiac comorbidities ( 1 ).
How long after MI can I start resistance training?
Low-level resistance training (eg, use of elastic bands, very light hand weights, and wall pulleys) should not begin until 2 to 3 weeks after MI. 13 The recommended beginning resistance exercise is with 1- to 2-lb dumbbells or wrist weights.
Which exercise imposes primarily a volume load on the myocardium?
Thus, aerobic exercise imposes primarily a volume load on the myocardium. 16. Isometric exertion involves sustained muscle contraction against an immovable load or resistance with no change in length of the involved muscle group or joint motion.
How long after CABG can you stretch?
Stretching or flexibility activities can begin as early as 24 hours after CABG or 2 days after MI. Patients are seen once a day (generally by a physical therapist, exercise physiologist, or nurse clinician) and can perform 10 to 15 repetitions to an RPE of 11 to 13 (light to somewhat hard).
What is the physiological response to dynamic aerobic exercise?
The physiological response to dynamic aerobic exercise is an increase in oxygen consumption and heart rate that parallels the intensity of the imposed activity and a curvilinear increase in stroke volume. There is a progressive increase in systolic blood pressure, with maintenance of or a slight decrease in the diastolic blood pressure, and a concomitant widening of the pulse pressure. Blood is shunted from the viscera to active skeletal muscle, where increased oxygen extraction widens the systemic arteriovenous oxygen difference. Thus, aerobic exercise imposes primarily a volume load on the myocardium. 16
What are the exercises used in ROM?
The ROM exercises used in the inpatient program for the surgery patient typically include shoulder flexion, abduction, and internal and external rotation; elbow flexion; hip flexion, abduction, and internal and external rotation; plantar flexion and dorsiflexion; and ankle inversion and eversion.
How does stretching improve strength?
In contrast to resistance training, stretching as an isolated activity increases neither muscle strength or endurance, but it should be incorporated into an overall fitness regimen. Considerable evidence suggests that stretching exercises increase tendon flexibility, improve joint range of motion (ROM) and function, and enhance muscular performance. 9 Moreover, observational studies support the role of flexibility exercise using ballistic (movement), static (little or no movement), or modified proprioceptive neuromuscular facilitation techniques 9 in the prevention and treatment of musculoskeletal injuries. 21 These promote a transient increase in the musculotendon unit length that results from actin-myosin complex relaxation and a lasting increase through alteration in the surrounding extracellular matrix. Thus, aerobic and/or resistance training should be complemented by a stretching program that exercises the major muscle or tendon groups at least 2 to 3 days per week. 9
Is resistance training good for health?
Health and Fitness Benefits of Resistance Training. Although resistance training has long been accepted as a means for developing and maintaining muscular strength, endurance, power, and muscle mass (hypertrophy), 12 its beneficial relationship to health factors and chronic disease has been recognized only recently.
What is resistance training?
The goals of resistance training are to increase the amount of lean muscle on your body, and improve your ability to complete your daily activities such as shopping, house cleaning, yard work, and hobbies.
How to reduce pain from exercise?
The injury risk can be reduced by beginning the program at a lower level and gradually increase your time and how hard you work. Add 5 minutes to your exercise time per week or every other week, and try to remain in your THZ or RPE level. Non-weight bearing activity (cycling, swimming, rowing) as opposed to weight-bearing activity (running or jumping-type activities) can help reduce the risk of injury.
How to reduce heart rate after eating?
This helps to avoid scheduling issues that may put off exercise for another time. Try to avoid exercise immediately after a meal (for at least 1 hour) due to the body’s high demand for blood during digestion. This will elevate your heart rate and reduce the level of exercise you may do. Noontime may work well for some, and can add a much-needed break to the day as well as help to avoid heavy lunches. Early evening exercise may help a person to unwind and relax after a hard day. Try to avoid exercising immediately before bedtime. This may make getting to sleep difficult. Other things to consider are medicines you take and how they affect you (heart rates, blood sugar levels, bathroom breaks) and how you may need to change you activity.
How to keep your body cooler during exercise?
Choose clothing that is suitable for the activity, location, and weather such as shorts and a t-shirt in warm conditions and layered clothing in cool to cold conditions. You may consider clothing that wicks sweat away from your body as you exercise. This will help to keep your body cooler in warm conditions and warmer in cooler conditions. Layering your clothing allows you to “peel off” the layers in cooler weather as your body heats up during your activity.
What does aerobics do?
The word aerobic means needing air or oxygen. Your body uses oxygen during exercise to produce “fuel” so you may continue the activity. This “fuel” production includes burning calories in the form of fat stored on the body as well as carbohydrates. During exercise, you continue to produce fuel and use the fat stores to help you with your weight loss goals.
What is cardiac rehab?
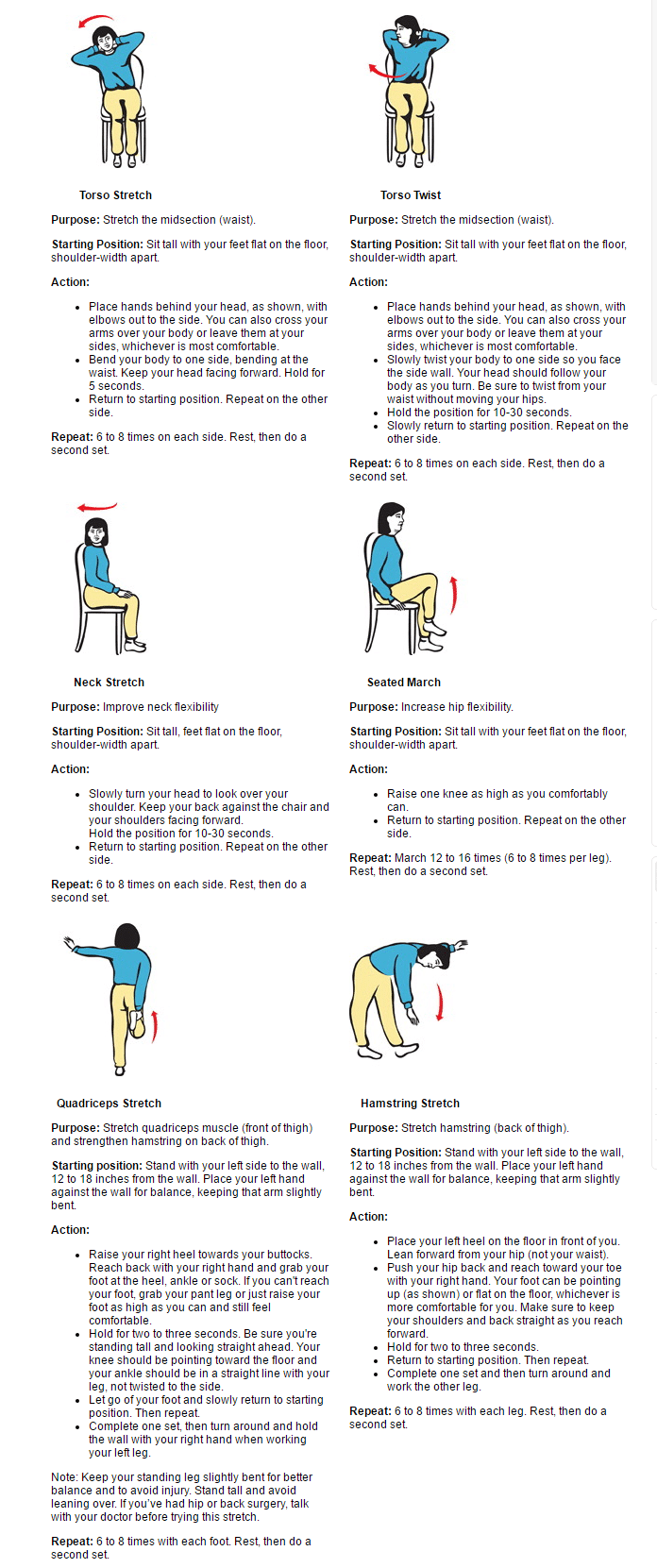
Cardiac rehabilitation is a program designed for people with heart problems. It helps you improve your cardiovascular (heart) health through proper nutrition, exercise, and stress relief. Get your heart pumping and improve your health with this key component of cardiac rehab, exercise! Stretching Exercises. Cardiovascular Exercises.
What is the role of a physical therapist in cardiac rehabilitation?
During cardiac rehabilitation, your workouts will be done under the supervision of a physical therapist, exercise physiologist, or nurse. The medical professional will guide you through specific exercises and monitor your vitals.
What are the three parts of cardiac rehabilitation?
Cardiac Rehabilitation Exercises. Your rehabilitation exercises will consist of three key parts: a stretching/warm up portion, cardio exercises, and strengthening exercises. Here are some sample exercises that you may do in rehab or incorporate into your program at home.
What are some exercises to strengthen your heart?
Cardiovascular Exercises . After you warm up and stretch, you’ll be ready to tackle cardio exercises. These aerobic exercises get your heart to pump harder and faster and strengthens your heart muscle. Get started with these exercises that you can perform in rehab or at home.
How to warm up muscles before working out?
A proper warmup is important before you start working out. Prepare your muscles by taking a 5-10 minute brisk walk or jog so your muscles are “warm” before stretching. Stretch to keep your muscles flexible with these TheraBand Stretch Strap exercises. The strap is a great aid for dynamic contract-release stretching.
How to stretch hamstrings?
Lie on your back with one knee bent. Place your other foot in a loop in the Stretch Strap, holding the end of the strap in both hands. Keep your leg in the strap straight and push your foot down against the strap’s resistance. Then breathe out and pull the strap and your leg toward your head to stretch your hamstring.
How to get a good workout?
Go workout on your lunch break before eating your lunch. Add physical activity to your regular routine, for example, go for a walk with your friend instead of meeting for coffee. If you don’t feel well…. Make an exercise plan as soon as you’re ready to leave the house.
How to get into cardiac rehab?
Here’s how to get going and make the most of cardiac rehab: 1 Ask your doctor if you are eligible . 2 If you are, register for a cardiac rehab program. 3 In consultation with your medical team, set goals for your heart health. 4 Work together to create a cardiac rehab plan. 5 Take an active role in your care to achieve your goals. 6 Keep taking your medicines correctly. 7 Call 911 if you experience new or worsening symptoms.
How to start a cardiac rehab program?
If you are, register for a cardiac rehab program. In consultation with your medical team, set goals for your heart health. Work together to create a cardiac rehab plan. Take an active role in your care to achieve your goals. Keep taking your medicines correctly.
Do you have to go to heart rehab alone?
You don’t need to face heart disease alone. Cardiac rehab is a team effort. You’ll partner with doctors, nurses, pharmacists – plus family and friends – to take charge of the choices, lifestyle and habits that affect your heart.