Medial Collateral Ligament (MCL) Sprain Rehabilitation Exercises Therapy
- Clam exercise: Lie on your uninjured side with your hips and knees bent and feet together. ...
- Straight leg raise: Lie on your back with your legs straight out in front of you. ...
- Side-lying leg lift: Lie on your uninjured side. Tighten up the front thigh muscles on your injured leg and lift that leg 8 to 10 inches (20 to 25 centimeters) ...
Full Answer
How should a MCL sprain be treated?
Sep 24, 2021 · Treatment Options for an MCL Sprain. RICE Principle. Following your injury, the RICE principle is commonly recommended to get the inflammation around the sprained ligament under control. NSAIDs. Bracing. Physical Therapy. Surgery.
How to strengthen your MCL?
How do you make your MCL heal faster? Exercises to strengthen muscles are used to treat MCL tears, among other things. During exercising, it is recommended to use a protective knee brace. Treatment for Anterior Cruciate Ligament (MCL) Injury. Rest; the use of an ice pack to minimize swelling that occurs hours after the injury
How much will MCL injury treatment cost?
Feb 02, 2021 · MCL Injury Rehab Considerations. As previously discussed, the severity of injury to the MCL will dictate the course of rehabilitation. Nonoperative care has been the preferred treatment for most MCL injuries again due to the high quality of tissue healing. If upon an initial evaluation from a physical therapist or orthopedist, the specific clinician observes there is …
Does a MCL tear heal able on its own?
Mar 02, 2022 · MCL Sprain Exercises. MCL sprain exercises should form part of a full rehabilitation program. Mobility, stretching, strengthening, proprioception, functional and sports specific exercises should all be included. We always recommend seeking professional advice before starting any medial ligament strengthening exercises.
How do you treat a strained MCL?
Most MCL injuries can be treated at home with rest, ice, and anti-inflammatory medicine. Your doctor may suggest that you use crutches and wear a brace that protects but allows for some movement of your knee. You may need to reduce your activity for a few weeks.
How long does it take to recover from a sprained MCL?
It can take anywhere from a few days to 8 weeks for an MCL injury to heal and a person to return to normal activities and sports. Generally, the timeline is determined by the severity of the injury, although this is not true for every person.
How do you heal a sprained MCL fast?
Early treatment for MCL injuries includes: Rest. Application of an ice pack application to reduce swelling that occurs hours after the injury. Compression using an elastic bandage or brace....Treatment for MCL tears include:Exercises to strengthen muscles.Use of a protective knee brace during exercise.Limited activity.Sep 26, 2016
Can I exercise with MCL sprain?
weeks following injury, the pain is usually subsiding and the swelling is lessened. You can now try to stretch the knee to regain motion. Stationary cycle, swimming (flutter kick only) and the following exercise program are recommended.
How do you tell if MCL is sprained or torn?
Symptoms of MCL Sprains and TearsA “popping” sound when the injury occurs. ... Immediate sharp pain from the inner section of the knee.Immediate swelling at the inner knee. ... Tenderness around the inner knee. ... Increased pain a few hours after the injury.More items...
Can MCL heal itself?
Can an MCL tear heal on its own? A grade 1 MCL tear (minor tear) can usually heal on its own with rest within one to three weeks. Grade 2 and grade 3 MCL tears, which are more severe, need proper treatment in order to heal, which can include resting, wearing a knee brace and doing physical therapy.Oct 18, 2021
What does MCL tear feel like?
MCL injuries hurt. Most people feel pain along the inside edge of the knee, and they also have swelling. You might hear a pop when the damage to the knee takes place, and your knee may lurch to the side. You may find it hard to walk, or feel like you can't put pressure on the leg with the hurt knee.Dec 18, 2020
Should you walk on a sprained ligament?
A grade 1 sprain causes little damage to the ligaments, and although the ankle will be tender for a few days, you can walk on it after a short period of rest. At grade 2 sprain, there is some tearing of the tissues and a longer recovery time of up to 4 weeks.Jun 5, 2018
Will walking on a torn MCL make it worse?
If the MCL or ACL tears, the result is usually pain, swelling, stiffness, and instability. In most cases, the injured person can still walk with the torn knee ligament. But the movement will be severely limited, not to mention painful. Surgery may be the best route to a pain-free life, with amazing success rates.
What helps ligaments heal faster?
Balance, control, and strengthening exercises can also help your ligaments heal more quickly than they otherwise would.
Is bike riding good for MCL injury?
You may ride the stationary bicycle daily for 10 to 20 minutes. Avoid using stair-stepper machines, doing deep knee bends and squats or any exercise that causes crunching, clicking or pain at the kneecap.
What is the middle phase of MCL rehab?
In the middle phase of MCL rehab, you will begin to re-expose the MCL to loads it will need to handle with everyday activities or sports you participate in. This includes progressive stability exercises focusing on joint proprioception, which is your body’s ability to understand where it is in space.
How long does it take to recover from a MCL tear?
However, most athletes return within 6 to 8 months time.
What is a P rehab program?
The Knee [P]Rehab Program is a physical therapist developed, step-by-step program that teaches you how to optimize your knee health. This 3-phase program will expose you to various knee and lower body strengthening and stabilization exercises supported by science. This program will bulletproof your knees for anything life throws at you! Learn more HERE!
Why are ligaments important?
In this way, ligaments provide support and strength to a joint, preventing injuries such as dislocations or instances of instability. As such, ligaments are present at almost every joint in our body. Some joints, like our hip joint, have what is called a good bony fit.
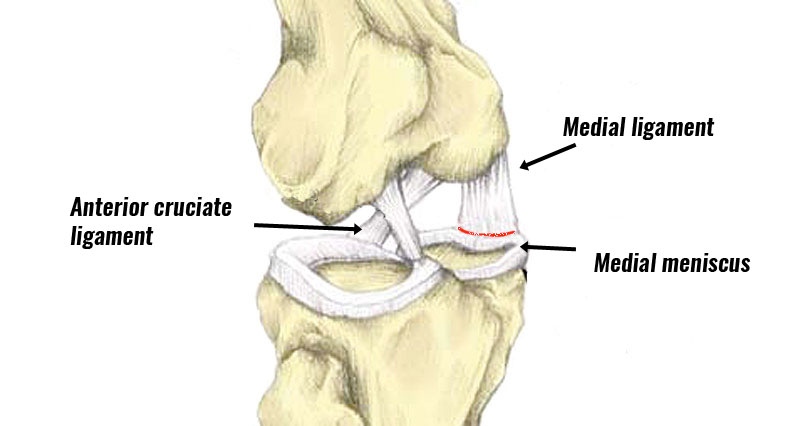
What is the MCL?
One of the more commonly injured knee ligaments is the Medial Collateral Ligament (MCL). The MCL is on the inside part of the knee and runs from the medial epicondyle of the femur to the medial aspect of the proximal tibia. The MCL provides stability and support to the knee during lateral or cutting movements.
How long does it take for a ligament to heal?
For instance, a grade I ligament sprain may take up to 4 weeks to heal; however, a grade II can take up to 4 months! It is important to know that these are averages of tissue healing times, and there are many more prognostic indicators that play a role in establishing healing times, which vary from person to person. Moreover, these timelines are based solely on the biological properties of the tissue. Understanding the basics of differences in healing times will help you gain perspective when recovering from an injury. You can read more on this topic below in our tissue healing article!
Why do you wear a knee brace?
This includes reducing swelling, modulating pain, and avoiding activities that will stress the MCL. In some instances, if there is a grade II or III injury, a brace may be worn for a period of time to help control the stability of the knee.
How long does it take to recover from a MCL sprain?
A mild MCL injury or grade one sprain should take 3 to 6 weeks to make a full recovery. A more severe grade 2 or grade 3 injury may take 8 to 12 weeks. MCL rehabilitation program.
What is the MCL?
Anatomy. The medial collateral ligament (or MCL for short) connects the thigh bone (or femur) to the shin bone (or tibia) on the inside of the knee and prevents the knee joint from moving sideways, particularly from forces on the outside of the knee. The MCL itself has two parts to it; a deep section which attaches to the cartilage ...
What is a medial knee sprain?
Medial Knee Ligament (MCL Sprain) A Medial collateral knee ligament sprain or MCL sprain is a tear of the ligament on the inside of the knee. It is usually caused by twisting or direct impact, but may develop gradually over time through overuse. Here we explain the symptoms, causes, treatment and rehabilitation of an MCL sprain.
How to reduce swelling in a swollen ear?
Electrotherapy. A professional therapist may use electrotherapy treatments such as Ultrasound to help control swelling and pain. Ultrasound transmits high frequency sound waves into the tissues applying a mico massage effect and helping to reduce swelling.
Where is the MCL located?
The MCL itself has two parts to it; a deep section which attaches to the cartilage and capsule in the knee, and a superficial band that starts higher up on the femur to an area lower down on the inner surface of the tibia and is much more near the surface .
Can a knee sprain cause a tear?
Twisting the knee can also cause a medial ligament sprain as well as the possibility of an ACL tear. If the foot is planted and the player tries to turn quickly this can also lead to stressing the joint causing the inside of the joint to open and tear the ligament.
What sports have medial ligaments?
Medial ligament injuries are common in contact sports such as football, rugby, and martial arts but they can also occur in activities of daily living as a result of falls that include a twisting action of the knee joint.
What are some exercises to help with MCL sprain?
MCL sprain proprioception exercises. Proprioception or movement control exercises involve balance and coordination which is often damaged with knee injury. Standing on one leg with your eyes closed is one way of measuring this.
How to straighten knees?
Contract the quadriceps muscles at the front of the thigh. Hold for 10 seconds. Relax and rest for 3 seconds. Repeat 10 to 20 times. You can also perform this exercise with a rolled up towel or foam roller under the knee as shown. Contraction will cause the foot to lift off the floor as the knee straightens.
How to do ROM?
To perform this gentle knee range of motion or ROM exercise the athlete lies on their back on a hard surface. The heel is slowly moved up towards the buttocks, as far as is comfortable. Socks can be worn to ensure that the foot slides. After a minute or so, a further movement may be possible. A towel or strap wrapped around ...
Who is Mike Walden?
Mike Walden. Mike is creator & CEO of Sportsinjuryclinic.net. A qualified Sports Injury Therapist with a degree in Physical Education, Sports Science and Physics, and a Postgraduate Certificate in Education.
What is plyometric exercise?
Plyometrics or plyometric exercises are a form of strengthening exercise, incorporating jumping, bounding and hopping movements, which works to increase power in the muscles. Power is used in the vast majority of all sports and so plyometrics can be used to help develop this for most athletes.
What is a foam roller?
A foam roller is an excellent piece of kit which can be used in place of massage to treat calf injuries. They are also excellent when use regularly as part of your warm up to help prevent future injury and improve performance.
How to get a calf raise?
Calf raises. Stand with feet shoulder-width apart and close to something to hold on to for balance. Lift your heels up as high as possible off the floor. In the early stages, this exercise must be done with both legs at the same time. Slowly lower back to the floor. Aim for 2-3 sets of 15-20 repetitions.
What is the purpose of the MCL handout?
This handout is to help you rebuild the strength of the knee muscles after injury to the MCL of the knee. It is intended as a guideline to help you organize a structured approach to strengthen the knee.
How to straighten knees?
Standing sideways to the step, slowly step up onto the step and slowly straighten the knee using the quadriceps muscles. Slowly lower the opposite foot to touch the floor. Do not land on the floor, just touch gently and repeat the step up.
How long does it take to recover from a MCL tear?
When this happens, you may face a recovery time of weeks to months, depending on the grade of the MCL tear. 2 . Treatment of an MCL tear depends on the severity of the injury.
How long should I be immobilized after a grade 3 MCL tear?
When a grade III MCL tear occurs, patients should brace their knee and use crutches until the pain has subsided. 7 The knee can be immobilized for a few days initially, but early range-of-motion will help in the recovery process.
How long does it take for a knee ligament to heal?
When this happens, you may face a recovery time of weeks to months, depending on the grade of the MCL tear.
Do MCL tears need surgery?
MCL tears often do not need surgery. There are many studies that document successful nonsurgical treatment in nearly all types of MCL injuries. 8 Most surgeons agree that for patients who complain of persistent knee instability, despite appropriate nonsurgical treatment, surgery is reasonable. 9
Can you bend your knee with a knee brace?
When a grade II MCL injury occurs, the use of a hinged knee brace can be useful in early treatment. 5 The hinged knee brace will allow you to bend the knee, but provide support to the injured ligament.
How to treat a MCL tear?
Nonsurgical Treatment Options for MCL Tears or Sprains. Most everyone who has an MCL injury will be advised by a health care professional to follow the RICE method: Rest. Activities that irritates the knee, such as pivoting and walking for long periods of time, should be avoided until the symptoms get better. Ice.
How long does it take for a MCL tear to heal?
MCL Tear or Sprain Nonsurgical Recovery Time. It can take anywhere from a few days to 8 weeks for an MCL injury to heal and a person to return to normal activities and sports. Generally, the timeline is determined by the severity of the injury, although this is not true for every person. Grade I (sprain or overstretched) tears will typically heal ...
Can you treat medial collateral ligament injury?
Both nonsurgical and surgical treatment options may be used to treat injuries to the knee’s medial collateral ligament (MCL). The majority of people recover using nonsurgical treatments. 1 In some cases, such as severe tears in elite athletes or people with multiple knee ligaments injuries, surgery may be recommended.
How to stop swelling in knees?
Wearing a tight, elastic bandage around the knee can help stop swelling. Elevation. Keeping the knee propped up above the waist can help decrease swelling. In addition to the RICE method, a person may be advised to: Take a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medication (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen or naproxen.
Is PRP good for MCL?
Platelet rich plasma (PRP) treatment, a form of regenerative medicine, may be recommended to people with high grade MCL tears. There are no long-term, robust studies done on the effectiveness of PRP injections for MCL tears; however, some people have seen positive results. 2 PRP is not considered standard practice and is typically not covered by insurance.
How to get your knee to move forward?
Wear a knee brace that allows the knee to move forward and backwards but restricts side-to-side movement. Exercise to restore range of motion and increase strength. These exercises typically include gentle stretches and strengthening exercises.
How is MCL surgery performed?
MCL surgery is generally performed through small open incisions on the inner (medial) knee. Recovery time from surgery will depend on the severity of the injury, the type of surgery performed, and other factors, such as age and overall health.
What is a grade 2 MCL sprain?
A Grade II MCL sprain is caused by a greater valgus stress force. Physical findings include marked tenderness over the MCL, mild to moderate swelling and pain and laxity on valgus stress testing. The knee should be stable at full extension, with laxity only present at 30 degrees flexion. Rehabilitation guidelines are as follows:
What is grade 1 MCL?
A grade I (mild) MCL sprain has local tenderness on the medial femoral condyle or medial tibial plateau, with minimal swelling (Brukner & Khan, 2012). There will be pain but no laxity on valgus stress testing at 30 degrees knee flexion. Rehabilitation guidelines are as follows:
What is medial collateral ligament injury?
Medial collateral ligament injuries occur following a traumatic valgus force, often while the knee is slightly flexed. Edson (2006) provides a comprehensive overview of the current recommended conservative management of MCL injuries, I highly recommend all physiotherapists read this article. This blog aims to provide a succinct overview of the rehabilitation of MCL injuries, with the approach I use to return an individual to full function.
What is the focus of rehabilitation?
In summary, the focus of the rehabilitation is to ensure the correct muscle activation and joint alignment throughout any exercise. The chosen exercise isn't important, as long as the patient feels the muscle working in the correct area. Alicia.

Classification
Signs and symptoms
- For a grade 1 MCL injury, there may be mild tenderness on the inside of the knee but usually no swelling. The patient is likely to be able to walk or even run with minimal symptoms but not at 100% and they will likely experience some form of discomfort. When the knee is assessed using stress tests such as the valgus stress test, the ligament will feel stable with a hard end feel (no l…
Diagnosis
- The valgus stress test is a diagnostic test that is used in cases of suspected MCL injuries. The therapist takes hold of the leg, ensuring the knee is slightly bent (approx 30 degrees). They stabilize the thigh whilst applying outward pressure on the lower leg (tibia) and this stretches the medial ligament. Pain on the inside of the knee and or excessive movement (laxity) with an alter…
Structure
- The MCL itself has two parts to it; a deep section which attaches to the cartilage and capsule in the knee, and a superficial band that starts higher up on the femur to an area lower down on the inner surface of the tibia and is much more near the surface.
Clinical significance
- Injury to the MCL often occurs after an impact to the outside of the knee when the knee is slightly bent. The ligament on the inside of the knee becomes stretched and if the force is great enough, some or even all of the fibres will tear. A grade one tear consists of fewer than 10% of the fibres being torn. A grade 2 sprain is upwards of 10% but not a complete tear of the ligament as in a gr…
Cause
- Repetitive sideways forces on the knee (known as valgus forces) can gradually over time lead to an MCL sprain. For example, from kicking a football with the inside of the foot or from kicking in martial arts. However, pain on the inside of the knee which does not occur after a sudden injury should also be considered for pes anserine tendinopathy or bursitis.
Treatment
- Treatment can be considered in terms of immediate first aid during the acute stage and longer-term rehabilitation which will depend on the severity of the injury. Sports Physiotherapist Neal Reynolds explains the treatment and rehabilitation process that elite footballers would undergo. Immediate first aid in the form of the PRICE principles (Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation) shoul…
Prevention
- Wear a compression bandage or knee support to help reduce any swelling and protect the joint. A hinged knee brace is best particularly for grade 2 and 3 injuries. It is a strong knee support which has solid metal supports down the sides to prevent sideways movement of the joint and protect the knee ligaments whilst healing. More severe grade 2 and full grade 3 injuries may require a li…