
Can a herniated disc cause nerve root impingement?
In most cases, a degenerative spine condition related to the aging process has given rise to an anatomical abnormality, such as a bone spur or herniated disc. When attempting to mitigate debilitating nerve root compression symptoms, strengthening the core muscles of the body and improving flexibility generally are good places to start.
What is nerve root impingement and how is it treated?
the nerve roots. The bone spurs on the nerve roots can cause pain and weakness in the arms. The bone spurs and bulging disc pushing on the spinal cord can cause arm symptoms as well as pain and weakness in the legs, loss of balance with walking, and loss of bowel and bladder control. Pressure on the spinal cord is called cervical myelopathy ...
What is disc degeneration and nerve impingement?
Jul 24, 2017 · Nerve Impingement Syndrome. A trapped or compressed nerve can arise from sudden movement or any minor injury, and while the condition is troublesome causing pain, numbness or tingling in the arm, hand or finger etc, the condition is easily treated by mobilisation: gentle oscillatory movement applied at the correct spinal level by an experienced ...
What causes nerve root impingement of the spinal cord?
Tissues that surround the nerve are putting pressure on the nerves or nerve root which in turn results in sensations that can come in the form of mild, dull pain, sharp, heightened pain, a tingly feeling, numbness, or simply feeling off in general. Most of our patients come into our Seattle chiropractic office with nerve impingement causing pain in the neck or the mid, upper, and …
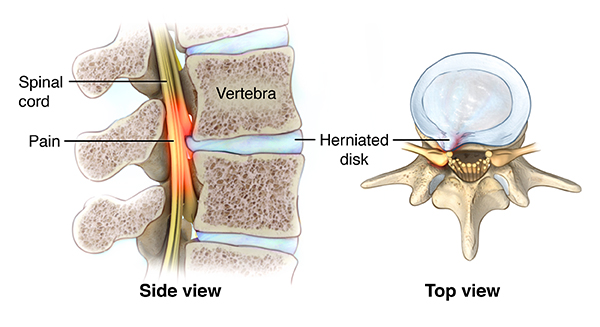
Is impingement the same as nerve root compression?
A pinched nerve is also referred to as nerve compression, nerve impingement, nerve root encroachment, radiculopathy and/or sciatica. However, all these terms don't mean the same thing. Nerve impingement, or nerve entrapment, indicates that one single nerve is directly compressed.Dec 17, 2019
What is nerve root impingement in lower back?
Lumbar radiculopathy refers to disease involving the lumbar spinal nerve root. This can manifest as pain, numbness, or weakness of the buttock and leg. Sciatica is the term often used by laypeople. Lumbar radiculopathy is typically caused by a compression of the spinal nerve root.
What does nerve root impingement mean?
Radiculopathy describes a range of symptoms produced by the pinching of a nerve root in the spinal column. The pinched nerve can occur at different areas along the spine (cervical, thoracic or lumbar). Symptoms of radiculopathy vary by location but frequently include pain, weakness, numbness and tingling.
Does nerve root impingement go away?
A pinched nerve that is caused by a herniated disc tends to resolve if given enough time and treatment. One study found that cervical radiculopathy caused by a herniated disc usually significantly improved within 4 to 6 months.
How long does nerve root compression take to heal?
Will a pinched nerve go away on its own? How long does it take? Yes, most will with time (normally four to six weeks). You can improve symptoms with rest and pain medications such as naproxen, ibuprofen or acetaminophen.Apr 7, 2020
What are the symptoms of L5 nerve root compression?
Compression or inflammation of the L5 and/or S1 spinal nerve root may cause radiculopathy symptoms or sciatica, characterized by:Pain, generally felt as a sharp, shooting, and/or searing feeling in the buttock, thigh, leg, foot, and/or toes.Numbness in the foot and/or toes.More items...
How is nerve root impingement treated?
The most common technique for treating nerve root impingement is through a spinal decompression procedure. This surgical technique aims to reduce pressure on the nerve root and give it more space to heal naturally.
How do you fix nerve impingement?
The most frequently recommended treatment for a pinched nerve is rest for the affected area. Your doctor will ask you to stop any activities that cause or aggravate the compression. Depending on the location of the pinched nerve, you may need a splint, collar or brace to immobilize the area.Jan 22, 2022
What does it feel like when a pinched nerve is healing?
During the process of healing nerve damage, the body part may feel unpleasant and tingly. Patients may also feel an electric shock-like sensation in the areas where nerve fibers are growing. These sensations may move around the affected area as during the healing of nerve damage.
What are the stages of nerve healing?
To achieve full recovery, the nerve must undergo three main processes: Wallerian degeneration (the clearing process of the distal stump), axonal regeneration, and end-organ reinnervation.
How do I know if nerve damage is healing?
How do I know the nerve is recovering? As your nerve recovers, the area the nerve supplies may feel quite unpleasant and tingly. This may be accompanied by an electric shock sensation at the level of the growing nerve fibres; the location of this sensation should move as the nerve heals and grows.
What happens if you let a pinched nerve go untreated?
Without proper treatment, a pinched nerve can develop into more serious conditions such as peripheral neuropathy or disc degeneration. You may also have general illness and chronic pain as a result of an untreated pinched nerve.Mar 15, 2021
Non-surgical methods of treatment
The goal of any treatment modality for spinal nerve compression is to mitigate the underlying cause of the compression. In most cases, a degenerative spine condition related to the aging process has given rise to an anatomical abnormality, such as a bone spur or herniated disc.
When surgery becomes an option
One reason people want to find out more about how to treat nerve root compression is that they are eager to avoid spine surgery. However, if conservative treatment methods prove ineffective after several weeks or months, your physician or spine specialist might recommend spine surgery.
What is cervical radiculopathy?
Cervical radiculopathy is defined as cervical nerve root compression. Many times, what causes this so-called compression is things like herniated disc material or arthritic bone spurs. It’s essentially the “sciatica” of the upper extremity.
What is the McKenzie method for cervical radiculopathy?
This is a diagnositic and treatment modality for mechanical issues of the spine and extremities of the body. This method is useful in diagnosing an individual who has neck pain to decipher if it is mechanical (meaning symptoms come from a musculoskeletal source), or if the clinical presentation is non-mechanical neck pain (meaning symptoms are coming from an underlying source that is NOT musculoskeletal). In addition, if a clinician does find that an individual’s neck pain is indeed mechanical, often times the McKenzie Method of diagnosis can be a guide for optimal treatment strategy.
What percentage of cervical radiculopathy is positive?
According to Wainner and colleagues, if 3 of the 4 tests are positive, there is a 65% of cervical radiculopathy. If 4 of the 4 tests are positive, it’s essentially a golden ticket and the probability jumps to 90%!
Is cervical radiculopathy a psychosocial disorder?
Furthermore, research has strongly indicated that psychosocial factors such as low self-efficacy and depression play a large role in determining how disabled one feels and plays a role in determining prognosis.
Is cervical radiculopathy a prognosis?
Speaking of prognosis, most patients with cervical radiculopathy have a favorable prognosis with non-surgical management. While re-occurrence is common, a large-scale epidemiology study found that at final follow-up, 90% of patients were asymptomatic or only mildly incapacitated by their symptoms.
Is manual therapy effective for cervical radiculopathy?
Manual therapy has been shown to be more effective than a wait-and-see approach (i.e. doing nothing) in countless studies. There are many different manual therapy treatments for cervical radiculopathy, including but not limited to cervical spine up glides, lateral glides, posterior-to-anterior mobilizations, manipulations, thoracic spine mobilizations and manipulation, and various soft tissue mobilizations. No one single intervention has been shown to be more effective than another; however, a multimodal approach incorporating many of the above manual therapy treatments in addition to therapeutic exercises and education has been shown to be the most effective cervical radiculopathy treatment approach of all.
Is cervical radiculopathy a multimodal treatment?
No one single intervention has been shown to be more effective than another; however, a multimodal approach incorporating many of the above manual therapy treatments in addition to therapeutic exercises and education has been shown to be the most effective cervical radiculopathy treatment approach of all.
What is nerve impingement?
Nerve impingement is a condition in which abnormal pressure is placed on the nerves in the cervical spine [neck] and is often related to degeneration of the discs. In order to understand the various problems that can occur in the cervical spine, you must first have an understanding of the anatomic structures involved.
What is the hole through which the nerve root exits the spine called?
The hole through which the nerve root exits the spine is called the neural foramen [NF]. Disc Degeneration, Nerve Impingement and Stenosis 1. Defining the Problem . Of all the parts of the cervical spine, it is the disc that leads to the majority of problems that can cause impingement of the nerves.
What is cervical stenosis?
Cervical Spinal Stenosis . There are two basic types of cervical stenosis, although some patients have both types. The first type of stenosis consists of symptoms in the neck and arms only caused by bone spurs on the nerve root. These patients are treated similarly to the patients with a cervical disc herniation.
How many bones are there in the cervical spine?
The cervical spine is composed of seven bones called cervical vertebrae. They are numbered 1 to 7 from the top to the bottom. They are referred to by their number. C1 is the top bone and C7 is the bottom bone. The vertebral body [VB] is the large, weightbearing part of the spine.
Why is the spinal cord so small?
Spinal stenosis is a condition in which the bone tunnel in which the spinal cord lies becomes too small because o. f degenerative changes to the disc and facet joints. When the disc degenerates, it loses height. This causes the tough oute. r part of the disc to . bulge [B] into the spinal cord area [the spinal canal].
Why does a degenerated disc wear out?
This can occur quickly because of a traumatic accident o. r slowly wear out over time as a process of aging. A worn out disc is called a degenerated disc. Not all degenerated discs cause problems, and in some respects disc degeneration is considered a normal part of the aging process.
How do bone grafts work?
The bone graft will fuse the two bones and the graft into the bone. A small titanium plate and screws are placed over the bone graft to connect the vertebral bodies above and below the graft together.
What is the term for a nerve root impingement?
This is referred to as nerve root impingement and can result in a common condition or set of symptoms known as radiculopathy . Radiculopathy is commonly described as symptoms of:
What causes a pinched nerve in the spine?
Foraminal stenosis causes the roots of the spinal nerve within the spine to become pinched, resulting in a variety of symptoms. Foraminal stenosis is commonly caused by a condition such as herniated discs due to an injury or bone spurs. Deuk Spine Institute offers nerve root impingement surgery, Deuk Laser Disc Repair, with a 95% success rate, ...
What is the best treatment for spinal stenosis?
Nerve root impingement, or spinal stenosis, is best treated with minimally invasive endoscopic laser spine surgery so that the cause of the impingement is repaired while retaining the disc and mobility of the patient.
Why does my nerve feel numb?
Altered sensation due to nerve irritation. Nerve root impingement when the pinched nerves cause radiculopathy . Delayed treatment may result in the nerve root becoming permanently damaged. This can result in irreversible weakness, numbness, paresthesias, pain or even atrophy of the muscles. The best treatment for nerve root impingement ...
Why does my spinal cord hurt?
The pain occurs when the spinal cord or spinal nerve is irritated by the pressure or a chemical reaction from the displaced herniated material. Loss of function, weakness, tingling, and pain can be caused when there is pressure from the herniated disc on the nerve roots. This is referred to as ‘nerve root impingement’.
Can a laser disc repair nerve root damage?
Without treatment the nerve root may become permanently damaged causing weakness, numbness, paresthesias, pain or even atrophy of muscles. Deuk Laser Disc Repair is a proven effective treatment of the discogenic causes of nerve root impingement. Learn more by watching the video below:
Does Deuk Spine Institute repair nerve roots?
Deuk Spine Institute offers nerve root impingement surgery, Deuk Laser Disc Repair, with a 95% success rate, small incision, and it does not damage or weaken the spine.
What is nerve impingement syndrome?
Nerve Impingement Syndrome. A trapped or compressed nerve can arise from sudden movement or any minor injury, and while the condition is troublesome causing pain, numbness or tingling in the arm , hand or finger etc, the condition is easily treated by mobilisation: gentle oscillatory movement applied at the correct spinal level by an experienced ...
Can muscle relaxers free nerves?
Pain killers and muscle relaxants will obviously never be able to free a trapped nerve. Sometimes manipulation is performed to break up adhesions (swathes of bonded flesh that have built up over time causing stiffness and devascularisation, and which affects nerves, resulting in pain).
Is spinal surgery necessary?
It can safely be said that for the vast majority of spinal conditions surgery is neither necessary nor effective, as it almost always leads to long term complications and suffering for the patient, out of all proportion to the original condition. The use of metal rods, screws and plates and the cutting away of parts of the spine, even the heating of discs to cause them to shrink (IDET procedure) represent a rather crude approach to the treatment of spinal problems and is not a method of ‘treatment’ that we can ever recommend.
How to know if you have a pinched nerve?
Some Common Signs and Symptoms To Keep In Mind If You Think You Are Dealing With a Pinched Nerve Include: Numbness. Decreased sensation. Sharp, aching, or burning pain (which may or may not radiate) Tingling (pins and needles) If a nerve is pinched for only a short amount of time, there is no risk of permanent damage.
Why do I have pinched nerves in my wrist?
However, pinched nerves can also appear in the hand, elbow, and wrist and this can be due to carpal tunnel syndrome. When a nerve impinges, it can be very painful, and if it’s not treated correctly, that pain can spread and cause even more harm. Using a holistic approach, Dr. Li can quickly determine the root of the problem ...
What causes pain in the back of the leg?
A bulged disc in your lumbar spine can put pressure on a nerve root, creating radiating pain down the back of your leg, but can also cause pain or discomfort throughout the back, hips, and buttocks. Schedule Your Complimentary Phone Consultation.
What is the term for a nerve that is too much pressure applied to a nerve?
Nerve Impingement. Nerve impingement , known to some as a pinched nerve, occurs where there is too much pressure applied to a nerve by surrounding tissues such as bone, tendon, cartilage, or muscles.
Can nerve damage cause numbness?
You probably felt a degree of numbness, tingling, or even weakness. As long as the pressure is relieved, nerve function returns to normal. However, if the pressure remains, chronic pain and nerve damage can ensue in the form of permanent sensation loss, loss of reflexes, and/or loss of muscle strength and tone.
Is MDT accurate for cervical herniations?
MDT is extremely accurate when diagnosing root problems and how to manage those problems.
Can a bulging disc in the neck cause pain in the arm?
A bulged disc at the cervical spine can present as radiating pain down your arm, a stiff and sore neck, and the pain and numbness can have a negative effect on your shoulder and arm by way of discomfort or over-compensating.
What is the best treatment for lumbar disc herniation?
Ninety percent of cases heal naturally with supportive therapy when the underlying cause is lumbar disc herniation. Supportive therapy includes several options, such as acupuncture, chiropractics, tricyclic antidepressants, pain medication, ...
What is the L5 and S1 nerve root?
What Is L5 and S1 Nerve Root Impingement? Impingement of a nerve between the L5 and S1 vertebrae indicates the structure is placing pressure on the nerve root. According to the Laser Spine Institute, this is one of the most common of all pinched nerves.
What is supportive therapy?
Supportive therapy includes several options, such as acupuncture, chiropractics, tricyclic antidepressants, pain medication, physical therapy and surgery. There are also minimally invasive surgical options available. WebMD indicates the pain is debilitating in some patients and infrequent and irritating for others.
Can numbness in the upper thigh be worse?
Infrequent pain has the potential to become worse. It is recommended that patients seek immediate attention if the lower extremities become progressively weaker, there is numbness in the upper thigh or the individual suffers loss of bowel or bladder control.
Can a pinched nerve cause burning?
According to the Laser Spine Institute, this is one of the most common of all pinched nerves. This nerve root feeds the sciatic nerve, and impingement has the potential to affect the lower buttocks, legs and feet. The Laser Spine Institute lists sciatica symptoms as pain, numbness, tingling and burning. In severe cases, sciatica causes muscle ...

Symptoms
Diagnosis
- While the definition of cervical radiculopathy is technically nerve root compression, there is increasing evidence that inflammation surrounding the nerve root is most responsible for the signs and symptoms that accompany cervical radiculopathy. Furthermore, there does not need to be signs of nerve root compression on imaging to make the diagnosis of cervical radiculopathy. …
Example
- These self-administered tests are not the exact same ones used in the Wainner cluster, but they are decently good enough to help you determine if you may have cervical radiculopathy. According to Wainner and colleagues, if 3 of the 4 tests are positive, there is a 65% of cervical radiculopathy. If 4 of the 4 tests are positive, its essentially a golden ticket and the probability ju…
Prevention
- We can EASILY do this by PREVENTING THOSE MOTIONS THAT CLOSE THE INTERVERTEBRAL FORAMEN, namely EXTENSION, ROTATION (turning your head) to the side, and SIDEBEND (tilting your head) to the side. All of these motions cause the IVF to get smaller, and subsequently compress the nerve root! So, if you have right sided cervical radiculopathy, STOP LOOKI...
Causes
- Furthermore, LOOKING UP is usually an aggravating position. Try your best to look up with your EYES and your thoracic spine. One of the worst things you can do at the computer is to let your head come forward. When you do so, you are essentially extending at the cervical spine to keep your eyes forward on the screen!
Treatment
- Manual therapy has been shown to be more effective than a wait-and-see approach (i.e. doing nothing) in countless studies. There are many different manual therapy treatments for cervical radiculopathy, including but not limited to cervical spine up glides, lateral glides, posterior-to-anterior mobilizations, manipulations, thoracic spine mobilizations and manipulation, and variou…
Purpose
- On the other hand, nerve tensioners entail elongating the nerve bed at two joints at the same time. While this may seem harmful at first glance, your nerves are meant to be move and elongated! The goal of nerve tensioners are to downregulate the nervous system and get it accustomed to nerve tension. However, in the acute stage when your pain levels are high, it is best to avoid nerv…
Prognosis
- Speaking of prognosis, most patients with cervical radiculopathy have a favorable prognosis with non-surgical management. While re-occurrence is common, a large-scale epidemiology study found that at final follow-up, 90% of patients were asymptomatic or only mildly incapacitated by their symptoms.