Symptoms
Rhabdomyolysis symptoms can range from mild to severe. Symptoms usually develop one to three days after the muscle injury, though some people may not even notice muscle soreness. The main signs of rhabdomyolysis include: Muscle swelling. Weak, tender and sore muscles. Dark urine that is brown, red or tea-colored.
Causes
Mar 17, 2021 · The “classic triad” of rhabdomyolysis symptoms are: muscle pain in the shoulders, thighs, or lower back; muscle weakness or trouble moving arms …
Prevention
Rhabdomyolysis is the rapid destruction of skeletal muscle resulting in leakage into the urine of the muscle protein myoglobin. Rhabdomyolysis has many causes. Medications can cause muscle injury and rhabdomyolysis. Rhabdomyolysis can cause muscle pain and weakness. Blood levels of muscle enzymes, including CPK, SGOT, SGPT, and LDH, as well as ...
Complications
Nov 25, 2021 · Trauma, heat, and exertion. Causes in this category include: a crush injury, which can occur when something heavy falls on you. a heat stroke. a …
Is there a cure for rhabdomyolysis?
Muscle cramps, aches, or pains that are more severe than expected. Dark urine (tea- or cola-colored) Feeling weak or tired, unable to complete job tasks or finish a workout routine. It is possible to have rhabdo and show no symptoms. If you do begin to show these symptoms, seek medical care immediately!
What is the best treatment for funicular myelosis?
Dec 15, 2019 · Funicular myelosis: therapy for folic acid deficiency. When funicular myelosis is caused by folate deficiency, 15 milligrams of folic acid per day are injected into the muscle. After three to five days can be switched to tablets, which must be taken two to three times a day. After about two weeks, the folic acid storage is usually filled.
What are the treatment options for transverse myelitis?
Oct 22, 2021 · Treatment funicular myelosis Treatment is aimed at stopping anemia and the process of demyelination of axons by intramuscular injections of vitamin B12 (cyanocobalamin) together with other B vitamins.More information in the article - Treatment of vitamin B12 deficiency [ 10] Prevention
What is rhabdomyolysis of the skeletal muscle?
Jan 19, 2022 · Treatment for transverse myelitis includes medications and rehabilitative therapy. Most people with transverse myelitis recover at least partially. Those with severe attacks sometimes are left with major disabilities. Products & Services Book: Mayo Clinic Family Health Book, 5th Edition Show more products from Mayo Clinic Symptoms

Can you recover from rhabdomyolysis?
Recovery from rhabdomyolysis varies and depends on the degree of muscle damage and the specific complications that occurred. If the condition is recognized and treated early, you can avoid most major complications and expect a full recovery.Jul 1, 2018
How long does rhabdomyolysis last?
It occurs after unaccustomed, and especially eccentric, muscular activity – such as descending a mountain. The soreness peaks after 2–3 days, but seldom lasts more than a week.Jun 13, 2019
What is the treatment for traumatic rhabdomyolysis?
To treat rhabdomyolysis, your doctor will first give you fluids and electrolytes intravenously (through a vein). These IV fluids flush the toxins from your system. You may need to stay in the hospital for a few days. After treatment, physical therapy can help you strengthen your muscles after an initial period of rest.Dec 4, 2019
What is the mainstay treatment for rhabdomyolysis?
The mainstay of treatment is hospitalisation with aggressive intravenous fluid (IVF) resuscitation with the correction/prevention of electrolyte abnormalities.Oct 1, 2007
Which is a key symptom of rhabdomyolysis?
The “classic triad” of rhabdomyolysis symptoms are: muscle pain in the shoulders, thighs, or lower back; muscle weakness or trouble moving arms and legs; and dark red or brown urine or decreased urination. Keep in mind that half of people with the condition may have no muscle-related symptoms.Mar 17, 2021
Can kidneys recover from rhabdomyolysis?
Ultimately, 8–65% of patients with rhabdomyolysis will require renal replacement therapy (RRT) [3,4,5]. After the episode, renal recovery is observed in most survivors but data on the risk of AKI to chronic kidney disease (CKD) transition in this specific setting are scarce [4, 11].Mar 2, 2020
Can rhabdomyolysis cause liver damage?
Abnormal liver function tests are frequently observed in cases of severe rhabdomyolysis. Typically, there is an increase in serum aminotransferases, namely aspartate aminotransferase and alanine aminotransferase.Mar 14, 2020
Why do I keep getting rhabdomyolysis?
The most common causes of single episodes of rhabdomyolysis are drugs, exercise and immobility. Defects in fatty acid β-oxidation are the most common metabolic myopathy to cause recurrent exercise-induced rhabdomyolysis.
What happens if rhabdomyolysis is left untreated?
Left untreated, or if not treated early enough, rhabdo can lead to irreversible muscle damage, permanent disability, kidney failure possibly requiring lifelong dialysis, and even death. Up to 8% of cases of rhabdomyolysis are fatal according to a NIOSH report.Nov 16, 2011
Can rhabdomyolysis cause permanent kidney damage?
Acute kidney injury develops in 10 to 55 percent of people with rhabdo. If major kidney damage occurs, it may be permanent. But kidney injury is not always severe, and treatment is possible.
Can rhabdomyolysis cause heart damage?
Rhabdomyolysis may cause severe damage to the human body because of acute renal failure, fatal heart rhythm disturbances, hypovolemic shock, disturbances of electrolyte balance, metabolic acidosis, hyperthermia, disseminated intravascular coagulation, etc. Drugs and toxins are the most common factors for the disease.
What kind of exercise causes rhabdomyolysis?
High intensity workouts from exercise classes like spinning and crossfit, as well as marathon-training and other grueling regimens, are supposedly to blame for an increasing portion of rhabdo cases.May 31, 2021
Why do you need a rhabdomyolysis surgery?
You may also need a surgical procedure (fasciotomy) to relieve tension or pressure and loss of circulation if compartment syndrome threatens muscle death or nerve damage. In some cases, you may need to be in the intensive care unit (ICU) to allow close monitoring. Most causes of rhabdomyolysis are reversible.
What are the symptoms of rhabdomyolysis?
The “classic triad” of rhabdomyolysis symptoms are: muscle pain in the shoulders, thighs, or lower back; muscle weakness or trouble moving arms and legs; and dark red or brown urine or decreased urination. Keep in mind that half of people with the condition may have no muscle-related symptoms.
What blood test can be used to diagnose rhabdomyolysis?
Confusion, dehydration, fever, or lack of consciousness. Blood tests for creatine kinase, a product of muscle breakdown, and urine tests for myoglobin, a relative of hemoglobin that is released from damaged muscles, can help diagnose rhabdomyolysis (although in half of people with the condition, the myoglobin test may come up negative).
What is rhabdomyolysis in kidneys?
Rhabdomyolysis is a serious syndrome due to a direct or indirect muscle injury. It results from the death of muscle fibers and release of their contents into the bloodstream. This can lead to serious complications such as renal ( kidney) failure. This means the kidneys cannot remove waste and concentrated urine.
What diseases can cause muscle toxicity?
Viral infections such as the flu, HIV, or herpes simplex virus. Bacterial infections leading to toxins in tissues or the bloodstream ( sepsis)
Can rhabdomyolysis be stopped?
And if rhabdomyolysis is related to a medication or drug, its use will need to be stopped or replaced with an alternative. After treatment, discuss with your doctor any needed limitations on diet or activity. And, of course, avoid any potential causes of rhabdomyolysis in the future. WebMD Medical Reference. Sources.
Is rhabdomyolysis reversible?
Most causes of rhabdomyolysis are reversible. If rhabdomyolysis is related to a medical condition, such as diabetes or a thyroid disorder, appropriate treatment for the medical condition will be needed. And if rhabdomyolysis is related to a medication or drug, its use will need to be stopped or replaced with an alternative.
Which muscle is affected by rhabdomyolysis?
heart muscle. The skeletal muscle is the muscle of movement of the body (moving the skeleton at the joints). Skeletal muscle is affected by rhabdomyolysis. Myoglobin is a protein component of the muscle cells that is released into the blood when the skeletal muscle is destroyed in rhabdomyolysis.
What are the complications of rhabdomyolysis?
One of the dreaded complications of rhabdomyolysis is kidney failure. This can occur for a variety of reasons. Direct injury to the kidney and plugging of the filtering tubes of the kidneys by the muscle proteins are among the causes of kidney function impairment in the setting of rhabdomyolysis.
What is the term for the rapid destruction of skeletal muscle resulting in leakage into the urine of the muscle protein
Rhabdomyolysis (RAB-DOE-MY-O-LIE-SIS) is the rapid destruction of skeletal muscle resulting in leakage into the urine of the muscle protein myoglobin. heart muscle. The skeletal muscle is the muscle of movement of the body (moving the skeleton at the joints). Skeletal muscle is affected by rhabdomyolysis.
What is the cause of muscle weakness?
Rhabdomyolysis can cause muscle pain and weakness. Blood levels of muscle enzymes, including CPK, SGOT, SGPT, and LDH, as well as blood and urine myoglobin are used to diagnose and monitor rhabdomyolysis. Hospitalization is sometimes required to treat rhabdomyolysis.
What is elevated myoglobin?
The levels of myoglobin can be elevated in blood and urine. The diagnosis of rhabdomyolysis is confirmed by detecting elevated muscle enzymes in blood, which include creatine phosphokinase (CPK), SGOT, SGPT, and LDH . The levels of these enzymes rise as the muscle is destroyed in rhabdomyolysis.
Is rhabdomyolysis reversible?
The overall prognosis of rhabdomyolysis is favorable as long as it is recognized and treated promptly. Most causes of rhabdomyolysis reversible. Severe cases of rhabdomyolysis may be associated with kidney damage and electrolyte imbalance and hospitalization and even dialysis can be required.
How to help rhabdomyolysis?
In mild cases of rhabdomyolysis, home treatment can help aid in the recovery process . The goals of at-home treatment include resting the body so muscles can recover and rehydration to help prevent further kidney damage. When you’re feeling fatigued, recline in a comfortable position and try to relax.
What is rhabdomyolysis in the body?
Rhabdomyolysis is the breakdown of damaged skeletal muscle. Muscle breakdown causes the release of myoglobin into the bloodstream. Myoglobin is the protein that stores oxygen in your muscles. If you have too much myoglobin in your blood, it can cause kidney damage. About 26,000 cases of rhabdomyolysis are reported in the United States each year.
How many cases of rhabdomyolysis are there in the US?
About 26,000 cases of rhabdomyolysis are reported in the United States each year. Most people with rhabdomyolysis are treated with fluids given through their veins in an intravenous (IV) drip. Some people may require dialysis or hemofiltration to address kidney damage in more severe cases.
What are the symptoms of rhabdomyolysis?
They’re not specific and may mimic other conditions. The symptoms of rhabdomyolysis include: muscle weakness. low urine output. fatigue. soreness. bruising.
What tests are done to determine if you have rhabdomyolysis?
They may also perform urine and blood tests to confirm a diagnosis of rhabdomyolysis. Tests to determine muscle and kidney health may include determining levels of: creatine kinase, which is an enzyme found in the skeletal muscles, the brain, and the heart. myoglobin in blood and urine, which is a protein that’s a byproduct of muscle breakdown.
Why do some people develop rhabdomyolysis?
Some people develop rhabdomyolysis because of genetic conditions such as problems with metabolism of. lipids or fats. carbohydrates. purines, which are in certain foods, such as sardines, liver, asparagus. Metabolic problems, such as the following, can also trigger rhabdomyolysis:
Can rhabdomyolysis cause kidney damage?
Even then, however, you may still have some lingering weakness and pain in your muscles. If major kidney damage occurs, your kidneys may be permanently damaged.
What does it feel like to have rhabdo?
If you develop rhabdo, you might have one or more of these symptoms: Muscle cramps, aches, or pains that are more severe than expected. Dark urine (tea- or cola-colored) Feeling weak or tired, unable to complete job tasks or finish a workout routine.
How long after muscle injury does rhabdo appear?
Seek medical attention when you have any rhabdo symptoms and be sure to ask to have your CK levels checked. Symptoms can appear any time after muscle injury. For some people, symptoms might not start to appear until several days after the initial injury. If you have any of these symptoms at any time, do not ignore them.
What is the brain affected by myelosis?
Funicular myelosis is a variant-rich disease. Especially affected is the spinal cord, but also the brain (encephalopathy). Damage to the brain is noticeable through cognitive impairment. The mental symptoms range from tiredness to dementia and psychotic symptoms.
Why is myelosis slow?
A vitamin B12 deficiency and thus a funicular myelosis are usually slow, because the body can store the vitamin in a relatively large amount (up to four milligrams). Since the daily requirement is only a few micrograms, the store can provide sufficient vitamin B12 for years.
What is the cause of myelosis?
Funicular myelosis is caused in most cases by a vitamin B12 deficiency (hypovitaminosis). Vitamin B12 (also called cobalamin) has many functions in the body. It is important for the nerve cells, red blood cells as well as the protein and nucleic acid metabolism. The nucleic acids are building blocks of the genome.
How much folic acid should I take for myelosis?
When funicular myelosis is caused by folate deficiency, 15 milligrams of folic acid per day are injected into the muscle. After three to five days can be switched to tablets, which must be taken two to three times a day. After about two weeks, the folic acid storage is usually filled.
Why is myelosis caused by lack of B12?
Most of the lack of vitamin B12 and thus the funicular myelosis are caused by insufficient intake of vitamin B12 in the gastrointestinal tract . This so-called resorption disorder occurs in 80 percent of cases due to the lack of a transport protein, which is required for the absorption of the vitamin.
How often should I take vitamin B12 for myeloma?
Subsequently, in the context of long-term therapy, the vitamin deficiency (and thus the funicular myelosis) with once or twice weekly or even once a month cobalamin injections are treated.
What is the best vitamin for funicular myelosis?
The disease usually begins insidiously with sensory disorders of the legs that lead to gait insecurity. Funicular myelosis is treated with vitamin B12. Read more about the symptoms, diagnostics and treatment of funicular myelosis.
Epidemiology
There are no data on the prevalence of funicular myelosis, but it is known that it usually affects people over forty years of age, and that in 95% of patients, the etiological factor of this syndrome is pernicious anemia, which is autoimmune in nature: the presence of antibodies to parietal cells of the stomach and to internal Castle factor, which ensures the absorption of vitamin B12 in the ileum..
Causes funicular myelosis
The main causes of funicular myelosis - demyelination of the nerve fibers of the funiculus or spinal cord columns - is a lack of vitamin B12 (cobalamin) in the body. [ 1]
Risk factors
Experts see the risk factors for the development of funicular myelosis in chronic deficiency of cobalamin in the body, the likelihood of which, in turn, increases with low stomach acidity ; hypoacid, atrophic or anacid gastritis with achlorhydria , as well as when part of the stomach is removed.
Pathogenesis
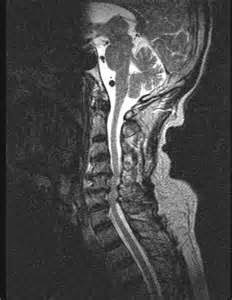
Explaining the pathogenesis of degenerative changes in the spinal cord , it should be noted that neurological manifestations in this condition are due to the defeat of the paired posterior (funiculus dorsalis) and lateral (funiculus lateralis) cords of the white matter of the spinal cord, consisting of processes (axons) of neurons.
Symptoms funicular myelosis
There are such types or forms of funicular myelosis: posterior columnar sensory ataxia or funicular myelosis with damage to the posterior cords of the spinal cord; pyramidal funicular myelosis - with damage to the funiculus lateralis, as well as mixed (with damage to the posterior and lateral cords). [ 5]
Complications and consequences
The most significant consequences and complications of funicular myelosis: neurological disorders, progressing to lower spastic paraparesis (paraplegia), and mental changes - up to partial cognitive dysfunction.
Diagnostics funicular myelosis
Routine diagnosis begins with recording the existing symptoms, examining the history, examining the patient, and examining reflexes .
What is the condition that causes myelin loss?
Neuromyelitis optica (Devic's disease) is a condition that causes inflammation and myelin loss around the spinal cord and the nerve in your eye that transmits information to your brain. Transverse myelitis associated with neuromyelitis optica usually affects both sides of your body. In addition to transverse myelitis, ...
Why is myelitis a transverse disease?
Sometimes there is no known cause. Viral, bacterial and fungal infections affecting the spinal cord may cause trans verse myelitis. In most cases, the inflammatory disorder appears after recovery from the infection.
How many episodes of transverse myelitis?
People with transverse myelitis usually experience only one episode. However, complications often linger, including the following: Pain, one of the most common debilitating long-term complications of the disorder. Stiffness, tightness or painful spasms in your muscles (muscle spasticity).
What is erythremic myelosis in cats?
Erythremic myelosis in a cat/Mielose eritremica em um gato. The more common variant, referred to as erythremic myelosis, and subsequently as erythroleukemia and erythroid/myeloid leukemia by others, is composed of immature erythroid and myeloid elements. Acute erythroid leukemia. More results ►.
What is the term for the abnormal proliferation of medullary tissue in the spinal cord?
A condition characterized by abnormal proliferation of tissue or cellular elements of bone marrow (e.g., multiple myeloma, myelocytic leukemia, myelofibrosis). 2. A condition in which there is abnormal proliferation of medullary tissue in the spinal cord, as in a glioma.
