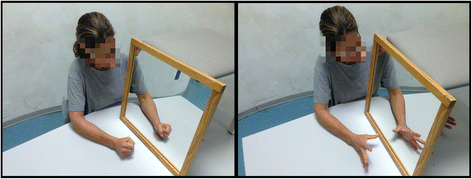
Mirror box therapy (MBT) is a relatively new therapeutic intervention that is gaining recognition within OT for the potential it offers in rehabilitation of upper limb function in stroke patients. It is postulated that mirror visual feedback can stimulate neural recovery in the brain using mirrored movements of the non-affected upper limb.
How to perform mirror therapy after stroke?
Feb 07, 2020 · In contrast to varied therapy approaches, mirror therapy (MT) can be used even in completely plegic stroke survivors, as it uses visual stimuli for producing a desired response in the affected limb. MT has been studied to have effects not just on motor impairments but also on sensations, visuospatial neglect, and pain after stroke.
How does mirror therapy for stroke rehab work?
Mar 06, 2020 · Mirror Therapy for Stroke Patients Overall, mirror therapy is a promising stroke rehabilitation method for stroke patients — especially those with hand or arm paralysis. It works by “tricking” the brain into thinking that you’re moving your affected side, even though it’s just a …
How does mirror therapy work?
Mirror therapy is a relatively new therapeutic intervention which is simple, inexpensive and most importantly patient directed treatment that focuses on moving the unimpaired limb. It was first introduced by Ramachandran and Roger Ramachandran to treat …
How to use mirror therapy for CRPS?
Jun 30, 2021 · Mirror therapy (also called mirror box therapy) is a form of neuromuscular treatment used to help people who have suffered a stroke to reduce pain and regain function in the affected upper extremity. The technique is also used to reduce phantom limb pain for amputees and to reduce chronic pain for people with complex regional pain syndrome and …

How does mirror therapy work for stroke patients?
Mirror therapy uses a mirror to create the illusion that the arm or leg affected by the stroke is moving. After a stroke, mirror therapy can improve movement in affected upper or lower limbs and activities of daily living, and appears useful as a supplement to other stroke rehabilitation activities.Feb 18, 2019
What is mirror therapy and how does it work?
Mirror therapy is a type of therapy that uses vision to treat the pain that people with amputated limbs sometimes feel in their missing limbs. Mirror therapy does this by tricking the brain: it gives the illusion that the missing limb is moving, as the person looks at the real, remaining limb in a mirror.Jul 3, 2019
How do you do mirror therapy?
Mirror Therapy involves viewing the unaffected limb in a mirror, while keeping the residual limb out of sight. To start, the individual observes the sound limb in the mirror, and then gradually begins to move the hand while continuing to watch in the mirror.Sep 14, 2020
How do you do mirror therapy at home?
How can I do mirror therapy at home?Place your affected arm behind a mirror so that when looking into the mirror the reflection of the unaffected arm appears in place of the hidden one.While looking into the mirror try to perform a series of basic movement exercises with both hands.Dec 13, 2018
How long does it take for mirror therapy to work?
Mirror therapy helps relieve this pain (after numerous sessions) by helping the brain recognize and “feel” the arm. As a result, the pain decreases in as little as 3 weeks.Mar 6, 2020
Who can benefit from mirror therapy?
At the end of treatment, mirror therapy moderately improved movement of the affected upper and lower limb and the ability to carry out daily activities for people within and also beyond six months after the stroke. Mirror therapy reduced pain after stroke, but mainly in people with a complex regional pain syndrome.Jul 11, 2018
How often should you do mirror therapy?
How often should I do mirror therapy? You should aim to complete four to five sessions a day, for five to ten minutes at a time. We recommend that you should keep a daily diary of your sessions and that you try to do your mirror therapy programme 'little and often' throughout the day.
How do you regain your hand after a stroke?
Repetitive hand exercises: Repetitive hand exercises are the most important step to hand recovery after a stroke. An occupational therapist will provide exercises that will strengthen the overall wrist, hand and fingers. It is important to perform these exercises as prescribed.Jul 11, 2019
How does mirror therapy work after stroke?
Mirror therapy offers an interesting method for regaining mobility after a stroke – even if the hand and arm are paralyzed. To understand how this process works, you’ll need to know about mirror neurons and neuroplasticity. We’re about to explain both. Then, at the end of this article, we’ll show you how to do mirror therapy – on your own ...
How to do a mirror therapy?
Here are the steps to perform mirror therapy: 1 Place a tabletop mirror over your affected arm and hand, with the non-affected arm laying on the table next to the mirror so that it is fully in view in the reflection. 2 Spend a few minutes observing the reflection and getting situated with the optical illusion. 3 It can be helpful to think of the mirror as a window, instead of a reflection. This can help further “trick” your brain into thinking that you’re viewing your affected side (even though it’s covered by the reflection of your non-affected side). 4 Then, practice simple hand therapy exercises with your non-affected hand. Some examples include touching your thumb to your fingertips, making a fist and then opening the hand, or turning your palm up and down. 5 Complete these exercises for at least 10 minutes, working your way up to half-hour sessions. Keep your eyes on the reflection in the mirror the whole time.
What happens to the brain after a stroke?
After a stroke, some of these pathways are damaged. Although you cannot revive the damaged brain tissue, neuroplasticity allows healthy parts of the brain to take over lost function. When the brain has trouble sending signals to the arm or hand after stroke, for example, neuroplasticity allows new areas of the brain to take over this function.
Why do mirror neurons fire?
As a result, your brain gets the feedback necessary to spark the rewiring process called neuroplasticity.
When my mom had a stoke on May 2, what side of her body was rendered useless?
When my 84-year-old Mom had a stoke on May 2, the right side of her body was rendered useless. In the past six months, she has been blessed with a supportive medical team, therapy team, and family team that has worked together to gain remarkable results.
How to get rid of a swollen hand?
Complete these exercises for at least 10 minutes, working your way up to half-hour sessions.
What is mirror therapy?
Mirror therapy (also called mirror box therapy) is a form of neuromuscular treatment used to help people who have suffered a stroke to reduce pain and regain function in the affected upper extremity. The technique is also used to reduce phantom limb pain for amputees and to reduce chronic pain for people with complex regional pain syndrome ...
How does mirror therapy work?
Mirror therapy uses visual feedback to take advantage of the brain’s neuroplasticity. The theory behind mirror therapy hypothesizes that the visual feedback from the mirror stimulates the mirror neuron system to reroute motor signals away from the damaged motor neurons and on to the motor cortex.
Is mirror therapy effective for stroke?
Treatment protocols and techniques for mirror therapy are hard to come by, but as seen by the evidence presented above, mirror therapy appears to be the most effective when used in combination with traditional stroke rehabilitation techniques.
How does mirror therapy help with stroke?
Mirror therapy uses a mirror to create the illusion that the arm or leg affected by the stroke is moving. After a stroke, mirror therapy can improve movement in affected upper or lower limbs and activities of daily living, and appears useful as a supplement to other stroke rehabilitation activities. Immediately after a stroke, about 80% of people ...
What is mirror therapy?
During mirror therapy, a mirror is used to create a reflection of an unaffected arm or leg in place of the affected limb (1;11) . When the unaffected limb is moved, the mirror image “tricks” the brain into thinking that the affected limb is moving (1;12).
How long does mirror therapy last?
Mirror therapy was carried out 3-7 times a week for 2-8 weeks, and for 15-60 minutes at a time . This review found that mirror therapy can be safe and effective. In fact, it improved upper and lower limb movement in affected limbs and the ability to conduct daily activities for up to and potentially beyond 6 months after stroke, ...
Who is the author of the blog?
Blog Posts are written by a professional writer, assessed for accuracy by Dr. Maureen Dobbins , an expert in interpreting and communicating the scientific literature, and edited by a professional editor. There are no conflicts of interest.
What is mirror therapy?
Mirror therapy exercises are designed to harness neuron mirroring to activate neurons in the affected area of the brain, and eventually increase the dexterity, accuracy, and velocity of impaired limbs. To help a patient begin a structured mirror therapy regimen, a medical professional will first describe mirror box therapy protocol, ...
How does mirror therapy work?
To induce this neural regeneration, mirror therapy must first activate the neuron mirroring network — a complex system involving mimicry and human learning.
What is the main cause of disability?
Strokes are one of the main causes of disability around the globe. Both hemiplegia (paralysis on one side of the body) and hemiparesis (muscle weakness on one side of the body) are common following a stroke. According to the Journal of Physical Therapy Science, about 85 percent of stroke survivors will suffer from hemiplegia, ...
Why is mirror therapy important?
Because mirror therapy is designed to treat motor impairment, it’s important to remember that this treatment is rooted in “the basic principles of motor learning: a high number of repetitions combined with variation of the movement performance,” according to Mirror Therapy: Practical Protocol for Stroke Rehabilitation.
How many people have a stroke every year?
Every year, 15 million individuals suffer strokes worldwide, and approximately five million of those who survive are permanently disabled as a result, according to the World Health Organization. Fortunately, mirror box therapy (MT) is a safe and effective pathway to enhanced motor function for many stroke survivors.
Is mirror therapy appropriate for stroke patients?
Mirror therapy requires specific physical and cognitive capabilities, which can make it inappropriate for some patients. Individuals with severe disabilities following a stroke, or as a result of another condition, may not be able to perform effective mirror therapy. Per mirror therapy protocol, treatment suitability is based on three overall dimensions: affective, cognitive, and physical abilities.
What is mirror therapy?
Mirror therapy or also called mirror therapy (MT) can be an alternative rehabilitation therapy to improve motor function in patients with hemiparese due to stroke. Besides being efficient, easy and economical, MT is proven to improve motor function after stroke. ...
Why do we need a practice based protocol?
Preface The main reason to develop a practice-based protocol was because mirror therapy is still inconsistently used in clinical situations and many physical and occupational therapists expressed a strong need for some form of guidance to structure therapy and support imple-mentation of mirror therapy in routine care .
Does MT help with stroke?
For stroke there is a moderate quality of evidence that MT as an additional intervention improves recovery of arm function, and a low quality of evidence regarding lower limb function and pain after stroke. The quality of evidence in patients with complex regional pain syndrome and phantom limb pain is also low.