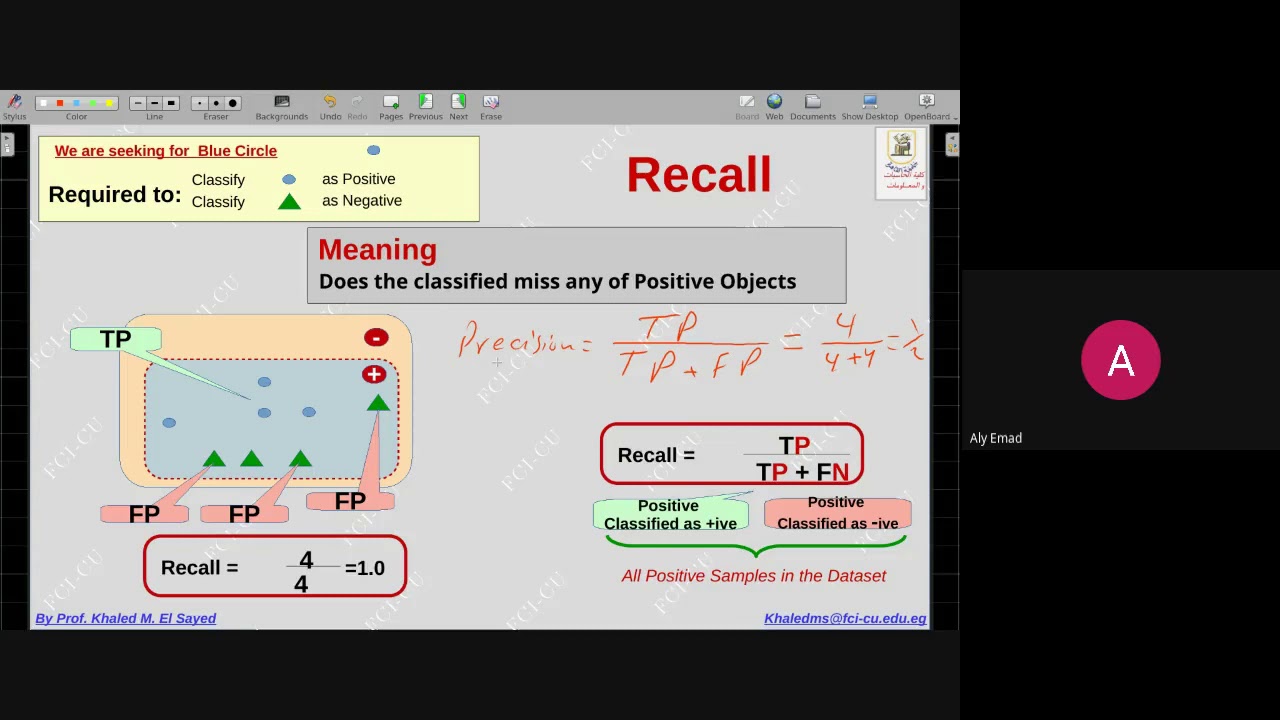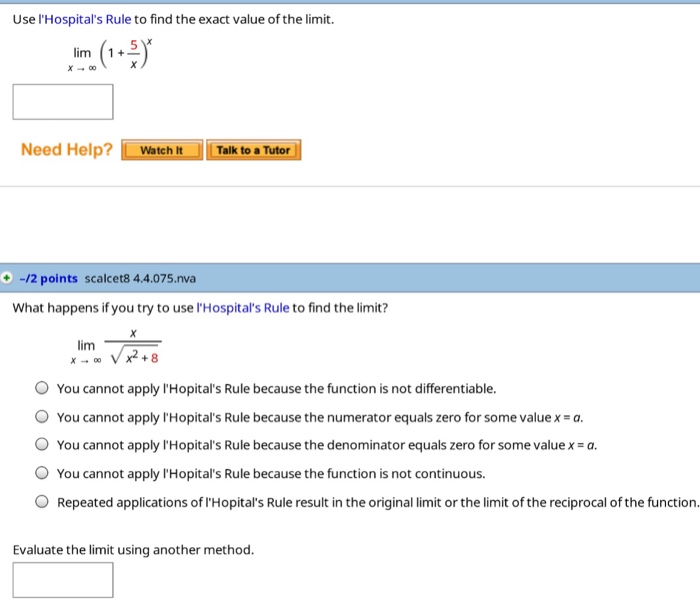
What are the different levels of treatment?
Levels of CareLevel 0.5: Early Intervention.Level I: Outpatient Services.Level II: Intensive Outpatient/Partial Hospitalization Services.Level III: Residential/Inpatient Services.Level IV: Medically Managed Intensive Inpatient Services.
What are the levels of mental health care?
A guide to understanding mental health levels of careInpatient. Inpatient is our highest level of care, which provides mental and physical stabilization during an acute episode. ... Residential. ... Partial hospitalization. ... Intensive outpatient. ... Outpatient.Jun 9, 2020
What is a Level 2 mental disability?
Level 2: SMI-A2 Meets criteria as a severely mentally ill individual, with or without a co-occurring substance abuse disorder, with currently mild and relatively stable signs and symptoms.
What is a 3.1 level of care?
Level 3.1 programs are appropriate for patients whose recovery is aided by a time spent living in a stable, structured environment where they can practice coping skills, self- efficacy, and make connections to the community including work, education and family systems.
What is the highest level of mental health care?
Acute inpatient treatment is also known as psychiatric hospitalization and is the highest level of mental health care. It's designed to help you get through a mental health crisis safely.Apr 27, 2021
How do I know if I need a higher level of care?
Typically, a higher level of care is recommended if a client has been unable to adequately address and change eating disorder behaviors necessary for recovery in an outpatient setting.Jul 19, 2017
How long is an inpatient mental health stay?
It turned out to be three weeks. The length of stay depends on your needs and can range from a few days to a few weeks and more. The amount of time you spend in an inpatient facility depends on your doctor's recommendation.Jul 26, 2021
What triggers a Level 2 Pasrr?
If an individual is suspected to have mental illness or an intellectual disability, a Level II evaluation is conducted to confirm this. A Level II must not merely rubber stamp the outcome of the Level I.
What is a Level 2 psych evaluation?
What is a Level II Evaluation? The Level II mental illness evaluation is an in-depth psychosocial evaluation of the individual. This evaluation is currently performed face-to-face or via telehealth at the facility where the individual is located, in an interview format.Apr 5, 2022
How long is an ASAM good for?
How long will the certification last? After a program is certified, CARF will annually require attestation to the elements of the certification. To continue certification beyond three years, the program will need to demonstrate satisfaction of the ratable elements through another survey.
What are the different levels of care for the treatment of substance use disorders?
Level I: Outpatient treatment. Level II: Intensive outpatient/partial hospitalization treatment (subdivided into levels 2.1 and 2.5) Level III: Residential/inpatient treatment (subdivided into levels 3.1, 3.3, 3.5, and 3.7) Level IV: Medically managed intensive inpatient treatment.
What does Asam Level 2 mean?
Level 2 encompasses services that are capable of meeting the complex needs of people with addiction and co-occurring conditions. It is an organized outpatient service that delivers treatment services during the day, before or after work or school, in the evening, and/or on weekends.
What is level 3.3 treatment?
First, treatment at this level can proceed at a slower pace but with more reinforcement to accommodate those who may be experiencing cognitive or other impairments. Cognitive conditions such as traumatic injury or alcohol-related brain damage are often interlinked with substance use disorder.
What is the first described level of treatment?
The first described level of treatment is designed for those who are at known risk for developing a substance use disorder. It’s also for people who have shown signs and symptoms of a substance use disorder but do not meet diagnosable criteria for it.
What is the ASAM level of care?
The ASAM Levels of Care describes five broad categories of treatment that vary in intensity, from least to most intensive.
How many hours of treatment is required for an IOP?
In an IOP, patients receive treatment for nine to 20 hours per week and have frequent contact with physicians, psychiatrists and therapists. Many intensive outpatient programs are provided for short periods during the day or on evenings and weekends.
How long does partial hospitalization last?
Treatment at facilities offering partial hospitalization services lasts for at least 20 hours per week. Individual, group and family therapy are major components of treatment, as is psychoeducation.
What is an IOP in medical?
Patients with more complex needs, such as those with a co-occurring disorder, may be eligible for an intensive outpatient program (IOP) or a partial hospitalization program (PHP). These programs are structured to treat patients more rigorously while offering more resources than outpatient services can provide.
What is residential treatment?
Residential treatment programs, or inpatient drug treatment programs, are for patients whose addictions have created significant functional impairments. It’s also for patients who require more stability than they can achieve at home. At this level, patients live on-site or in close proximity to their treatment.
What are some examples of rehabilitation?
Some examples of rehabilitation include: 1 Exercises to improve a person’s speech, language and communication after a brain injury. 2 Modifying an older person’s home environment to improve their safety and independence at home and to reduce their risk of falls. 3 Exercise training and education on healthy living for a person with a heart disease. 4 Making, fitting and educating an individual to use a prosthesis after a leg amputation. 5 Positioning and splinting techniques to assist with skin healing, reduce swelling, and to regain movement after burn surgery. 6 Prescribing medicine to reduce muscle stiffness for a child with cerebral palsy. 7 Psychological support for a person with depression. 8 Training in the use of a white cane, for a person with vision loss.
How does rehabilitation help?
It can help to avoid costly hospitalization, reduce hospital length of stay , and prevent re-admissions . Rehabilitation also enables individuals to participate in education and gainful employment, remain independent at home, and minimize the need for financial or caregiver support.
Why is rehabilitation important?
Rehabilitation is an essential part of universal health coverage along with promotion of good health, prevention of disease, treatment and palliative care . Rehabilitation helps a child, adult or older person to be as independent as possible in everyday activities and enables participation in education, work, recreation and meaningful life roles ...
Is rehabilitation a health service?
Misconceptions about rehabilitation. Rehabilitation is not only for people with long-term or physical impairments. Rather, rehabilitation is a core health service for anyone with an acute or chronic health condition, impairment or injury that limits functioning, and as such should be available for anyone who needs it.
What is a level 3 NICU?
A level 3 NICU cares for babies born before 32 weeks gestation, weigh less than 3 pounds, 5 ounces, have medical conditions or need surgery. Level 3 NICUs also provide a full range of respiratory support and have available subspecialists include neonatologists and staff and equipment to provide life support as long as necessary.
What is the name of the unit where a baby is born?
Some new parents find themselves grappling with unanticipated complications after their baby is born. If the baby has to spend time in the hospital, he or she likely will be in the neonatal intensive care unit, or NICU. That’s when parents may wonder what a NICU is and what’s the difference between levels of NICUs.
What is a NICU level?
The American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) developed standards for NICU designations to outline the type of care newborns can receive in a facility. Level 1 and 2 NICUs are designed to provide basic care for newborns with conditions ...
What is the highest level of NICU?
Some babies may need more complex care available at the highest level of NICU — level 4. To obtain a level 4 NICU designation, a hospital needs to meet all level 3 capabilities, plus have experience caring for the most complex and critically ill newborns.
What is level 3.7 in addiction treatment?
These services are differentiated from Level 4.0 in that the population served does not have conditions severe enough to warrant medically managed inpatient services or acute care in a general hospital where daily treatment decisions are managed by a physician. Level 3.7 is appropriate for adolescents with co-occurring psychiatric disorders or symptoms that hinder their ability to successfully engage in SUD treatment in other settings. Services in this program are meant to orient or re-orient patients to daily life structures outside of substance use.
What is level 3 in nursing?
Level 3 programs include four sublevels that represent a range of intensities of service. The uniting feature is that these services all are provided in a structured, residential setting that is staffed 24 hours daily and are clinically managed (see definition of terms above). Residential levels of care provide a safe, stable environment that is critical to individuals as they begin their recovery process. Level 3.1 programs are appropriate for patients whose recovery is aided by a time spent living in a stable, structured environment where they can practice coping skills, self- efficacy, and make connections to the community including work, education and family systems.
What is SBIRT level 0.5?
These early intervention services—including individual or group counseling, motivational interventions, and Screening, Brief Intervention, and Referral to Treatment (SBIRT)—seek to identify substance-related risk factors to help individuals recognize the potentially harmful consequences of high-risk behaviors. These services may be coverable under Medicaid as stand-alone direct services or may also be coverable as component services of a program such as driving under the influence or driving while intoxicated programs and Employee Assistance Programs (EAPs). Length of service may vary from 15 to 60 minutes of SBIRT, provided once or over five brief motivational sessions, to several weeks of services provided in programs. Medicaid coverage of services and component services, whether provided directly or through programs, must comport with all applicable rules, such as state plan benefit requirements.
How many hours of outpatient therapy is level 2?
Level 2.1 intensive outpatient programs provide 9–19 hours of weekly structured programming for adults or 6–19 hours of weekly structured programming for adolescents. Programs may occur during the day or evening, on the weekend, or after school for adolescents.
What is level 1 care?
Level 1 is appropriate in many situations as an initial level of care for patients with less severe disorders; for those who are in early stages of change, as a “step down” from more intensive services; or for those who are stable and for whom ongoing monitoring or disease management is appropriate. Adult services for Level 1 programs are provided less than 9 hours weekly, and adolescents’ services are provided less than 6 hours weekly; individuals recommended for more intensive levels of care may receive more intensive services.
What is intensive outpatient care?
Setting: Intensive outpatient programs are primarily delivered by substance use disorder outpatient specialty providers, but may be delivered in any appropriate setting that meets state licensure or certification requirements. These programs have direct affiliation with programs offering more and less intensive levels of care as well as supportive housing services.
What is residential treatment?
This gradation of residential treatment is specifically designed for specific population of adult patients with significant cognitive impairments resulting from substance use or other co-occurring disorders. This level of care is appropriate when an individual’s temporary or permanent cognitive limitations make it unlikely for them to benefit from other residential levels of care that offer group therapy and other cognitive-based relapse prevention strategies. These cognitive impairments may be seen in individuals who suffer from an organic brain syndrome as a result of substance use, who suffer from chronic brain syndrome, who have experienced a traumatic brain injury, who have developmental disabilities, or are older adults with age and substance-related cognitive limitations. Individuals with temporary limitations receive slower paced, repetitive treatment until the impairment subsides and s/he is able to progress onto another level of care appropriate for her/his SUD treatment needs.
What is recovery residence?
A good recovery residence provides a community-based environment to initiate and sustain recovery – defined as abstinence from alcohol and other non-prescribed drug use, and improvement in one’s physical, mental, spiritual and social wellbeing.
What is a halfway house in Florida?
The term ‘halfway house’ has come to mean different things in different parts of the country – for instance in Pennsylvania, a halfway house is a structured residential treatment center, whereas in Florida it might be a transitional residence following treatment. Additionally, the term halfway house tends to be associated with some stigma – there ...