
- Rest is vital. Sometimes, people will use crutches for a few days or a week to allow the most significant pain symptoms to subside.
- Ice on the calf muscle can ease pain, reduce swelling, and counteract inflammation. Ice is one of the most helpful treatments in the early phase of ...
- Compression can control swelling, support the muscle, and reduce spasms. Even a simple compression sock or sleeve can do wonders.
- Elevation is one treatment that many people tend to undervalue—until they lower the leg and try to stand up but can't because of swelling. Elevating ...
- Stand facing a wall with your hands on the wall at about eye level. Put your affected leg about a step behind your other leg.
- Keeping both heels on the floor, bend both knees. ...
- Hold the stretch for at least 15 to 30 seconds.
- Repeat 2 to 4 times.
How do you treat a torn calf muscle?
Nov 17, 2021 · Foam rolling of the calf complex can be beneficial in the early phase to enhance blood flow and start to mobilize the tissue that is irritated from the injury. Be sure to listen to your body and not push into significant symptoms of pain; however, some mild discomfort that is tolerable can be expected in the early phase with this technique.
What is a calf strain and how to treat it?
Feb 28, 2022 · Calf strain treatment Cold Therapy. Use a cold therapy and compression wrap to minimise any bleeding within the muscle. Cold therapy can be... Rest. In the early acute stage complete rest is important at least until you can walk pain-free. Once the acute phase... Compression. Wear a compression ...
Can rehabilitation of calf muscles improve performance?
The use of a compression sleeve for the calf was recommended to decrease the hemorrhaging. He was directed to apply ice to the area with 10 minutes on, 10 minutes off and then repeat for symptomatic relief. He was educated on the proper technique of elevating the limb slightly above the level of the heart to reduce the swelling.
How long does it take to rehab a calf strain?
Management and Treatment How are pulled calf muscles treated? Immediate treatment for pulled calf muscles usually includes RICE, which stands for: Rest: Stop running or physical activity to avoid further damaging the calf. Ice: Apply an ice pack or cold compress for 20 minutes every two hours. Don’t apply ice directly to your skin.
How do I strengthen my medial calf muscles?
The 4 Best Calf Strength ExercisesStraight Knee Calf Raises. Start with both feet on the ground near a wall or bench to hold on to. ... Bent Knee Calf Raises. Start with both feet on the ground near a wall or bench to hold on to. ... Seated Calf Raise. This can be performed on a seated calf raise at the gym. ... Hopping.
What is the fastest way to heal a calf muscle?
Treating a pulled calf muscleIce or cold compresses. Wrap these in a soft cloth and place on your calf for 10 minutes. ... Heat pads. ... Leg wraps. ... Prop your leg up above heart level. ... Rest for at least a full day. ... Take over-the-counter pain medications.
How long does it take for a partially torn calf muscle to heal?
In the less severe cases it usually takes up to three days for a pulled calf muscle to start feeling better. In the most severe cases that don't require surgery a full recovery may take up to six weeks. In the case that the injury requires surgery the recovery period may extend up to six months to a full year.
How do you train a medial calf?
10:2013:49Best Gastrocnemius and Soleus Exercises | Advanced Training #24YouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipYou can do them on a leg press machine you can do them on a vertical leg press machine you can doMoreYou can do them on a leg press machine you can do them on a vertical leg press machine you can do them on a horizontal leg press machine that's going to help transfer that weight into your hips.
Is cycling good for calf strain?
Initial treatment involves rest for 2-3 days after which you can often resume gentle cross-training, providing it's pain-free. This might include swimming, or cycling (with low resistance) but should avoid impact, heavy resistance or sudden movements.Sep 30, 2012
Why is my calf tear not healing?
0:585:44Why is My Calf Strain not Healing? - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipWhy is my calf strain not healing. And by far the most common reason has been because they've justMoreWhy is my calf strain not healing. And by far the most common reason has been because they've just not strengthened it to a high enough level to be able to do their sports.
Did I pull or tear my calf muscle?
Symptoms of a torn calf muscle can include: No calf strength, including being unable to balance or bear weight on the injured leg. Snapping or popping sensation in your calf. Sudden pain in the back of your lower leg, like someone kicked your calf.Aug 24, 2021
Should you massage a torn calf muscle?
The No HARM Protocol should also be applied – no heat, no alcohol, no running or activity, and no massage. This will ensure decreased bleeding and swelling in the injured area.Aug 10, 2017
What is the difference between a calf strain and a tear?
Symptoms. A calf strain usually starts with sudden pain in the back of the lower leg. A pop, snap or tearing sensation may be felt. Occasionally, with a severe tear, it may feel like you have been shot in the back of the leg.Mar 15, 2018
How do you activate your inner calf?
0:030:56How to Work Out Your Inner Calves - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipPosition want to start on my right foot turn my right toe inward. And as I balance on that foot. AndMorePosition want to start on my right foot turn my right toe inward. And as I balance on that foot. And I start to do my raise. I'll feel that my body weight shifts primarily over the ball of my foot.
How do I tone my inner calves?
Lift as high as possible on toes (plantar flexion) and pulse 3 times. Then lower heels just below step for calf and Achilles tendon stretch. This exercise is derived from barre training, and it tones the whole calf area. To "elevé," lift high on tippy toes with knees straight.Jul 12, 2016
Do lunges work calves?
Lunges don't require any equipment, and they're a great way to work your calves, glutes, hamstrings, and quads. They also help with balance and core strength. That's pretty efficient for one basic move!May 26, 2017
How to heal a strained calf muscle?
Reducing pain and symptoms may be achieved by off loading the strained calf musculature through rest, taping techniques, and appropriate soft tissue massage techniques. While somewhat lacking scientific evidence for soft tissue recovery modalities such as dry needling or western acupuncture can be popular amongst runners and may also be useful.
What is calf muscle strain?
Written by Brad Beer. ‘Calf muscle strains’ are a common running injury. They can be debilitating, painful, and require reduced or complete cessation from running. Short and longer lasting episodes of pain can stem from injury to the calf musculature.
Why does my calf hurt when I run?
The runner will typically report an acute onset of pain in the region of the calf brought on by activity, often times jumping or accelerating when running. For runners the injury more frequently arises during faster interval training, racing, or high-speed tempo runs.
Which muscle group is generating high peak forces across all speeds?
Furthermore when looking at peak muscle forces per muscle group across a variety of running speeds it is evident that the soleus muscle is generating high peak forces across all speeds, see image below:
Where does the majority of running force propulsion come from?
Greater than 50% of running force propulsion is generated from ‘below the knee’ plantar flexor musculature. Given the force developed by the calf it is understandable that the calf can be a potential site of muscular injury for a runner.
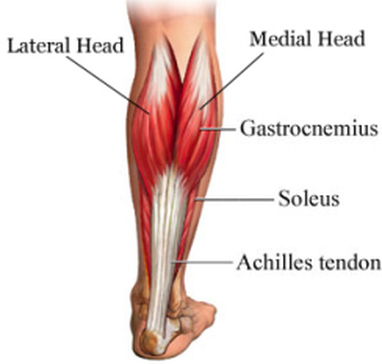
What muscle is the calf muscle?
Calf muscle anatomy. A calf muscle strain can occur to either of the two primary ‘calf muscles’; the soleus or the gastrocnemius (see anatomy images below): (i) soleus muscle. (ii) Gastrocnemius (medial and lateral heads) The muscles at the back of the leg are comprised of a superficial and a deep group of muscles.
Is high plantar flexor strength protective?
High plantar flexor function seems to be protective against achilles tendinopathy. Willy and Paquette in their review of masters runners state ‘runners with greater eccentric plantarflexor strength and greater propulsive forces during running have a reduced risk of developing achilles tendinopathy (9).
How to treat a torn calf?
A professional therapist may use Ultrasound to treat your torn calf. It transmits high-frequency sound waves into the tissue. This encourages blood flow, which facilitates healing of damaged muscle fibres. Ultrasound is particularly useful in the early stages of the injury.
How to tell if calf muscle is hurting?
Symptoms of a calf strain vary significantly depending on how bad your injury is. A mild strain may feel more like an ache during or after exercise. With a more severe strain, you will feel a sudden sharp pain at the back of the lower leg at the time of injury. Calf muscle strains are graded from 1 to 3, with grade 3 being the most severe.
Why do my calf muscles get tight?
Tight calf muscles – over time your muscles may tighten up and parts of the muscle may go into spasm, either from congenital reasons (genetics), or poor footwear. Wearing high heels. If you regularly wear high-heeled shoes this increases the risk of a number of injuries including calf strains.
What is a calf strain?
A Calf strain is simply a tear of one of the muscles which make up the calf muscle group at the back of the lower leg. The calf muscle group consists of the Gastrocnemius and Soleus muscles. The gastrocnemius is the big muscle at the back of the lower leg. The soleus is the smaller of the two and is located lower down and lies underneath ...
How to treat a swollen muscle?
Use a cold therapy and compression wrap to minimise any bleeding within the muscle. Cold therapy can be applied for 10 to 15 minutes every hour initially, reducing frequency as symptoms allow. Do not apply ice directly to the skin as it can cause ice burns. A simple reuseable gel pack with an elastic wrap is ideal.
Where is the soleus located?
The soleus is the smaller of the two and is located lower down and lies underneath the gastrocnemius. Both muscles contract to produce ‘plantar flexion’ at the ankle joint. This is the same movement as standing up onto your tip-toes.
Who designed the Calf Strain Rehabilitation Program?
Our Calf strain rehabilitation program has been designed by England & British Lions Rugby Sports Physiotherapist Phil Pask. It is based on what an elite athlete would do and adapted for people of all ages and abilities.
How to help calf pain?
Sometimes people will use crutches for a few days or a week to allow the most significant symptoms of pain to settle down. Ice: Icing the calf muscle can help with pain, reduce swelling, and ease inflammation. Ice is one of the most helpful treatments in the early phase of treatment. Compression : Compression can help to control swelling ...
What muscle is the calf?
The calf is made of three major muscles, the medial and lateral gastrocnemius and the soleus muscle. They unite to form the Achilles tendon to attach to the heel. The most commonly injured muscle when a calf strain occurs is an injury to the medial gastrocnemius muscle.
How to treat medial gastrocnemius?
Treatment of a medial gastrocnemius strain can usually be accomplished with simple steps. Initially, patients begin with typical " RICE " treatments of: 1 Rest: Avoid activities that cause pain. Sometimes people will use crutches for a few days or a week to allow the most significant symptoms of pain to settle down. 2 Ice: Icing the calf muscle can help with pain, reduce swelling, and ease inflammation. Ice is one of the most helpful treatments in the early phase of treatment. 3 Compression : Compression can help to control swelling and can also help support the muscle and reduce spasm. A simple compression sock or sleeve can help. 4 Elevation: Elevation is also beneficial to help swelling move out of the leg.
What is a medial gastrocnemius strain?
Diagnosis. Treatment. A medial gastrocnemius strain (MGS) is a specific type of injury to the calf muscle in the back of the leg. A muscle strain occurs when the muscle is stretched too far, which causes tears to occur within the muscle. A calf strain occurs when the muscle in the back of the leg sustains this type of injury.
How long does it take to recover from gastrocnemius?
Friction massage may help decrease adhesions. 4 . Typical recovery from a medial gastrocnemius strain is six weeks until return to athletic activities. You must be able to walk without pain before you are ready to return to exercise and sports.
What is calf injury?
Calf injuries are commonly seen in sports such as running, soccer, and tennis, and they can even be called "tennis leg.". 1 The gastrocnemius muscle crosses the knee joint and the ankle joint, flexing the foot and the leg.
How to help swelling in leg?
Ice is one of the most helpful treatments in the early phase of treatment. Compression : Compression can help to control swelling and can also help support the muscle and reduce spasm. A simple compression sock or sleeve can help. Elevation: Elevation is also beneficial to help swelling move out of the leg.
How to treat calf pain?
Rest: Stop running or physical activity to avoid further damaging the calf. Ice: Apply an ice pack or cold compress for 20 minutes every two hours. Don’t apply ice directly to your skin. Compression: Reduce swelling and fluid buildup by applying a compression bandage or wrap to the injured area.
What is pulled calf muscle?
What is a pulled calf muscle? A pulled calf muscle, or a calf muscle strain, occurs when the muscles in your calf — the soleus and gastrocnemius — get overstretched. The calf muscles are in your lower leg behind your shin bone and extend from the base of your thigh down to your heel. They help you flex and bend your foot, ankle and knee.
Why do I have calf strains?
Calf muscle strains usually occur when someone suddenly moves or overstretches their calf after standing still. Quick pivots, jumps or abrupt stops can cause strains. This injury is especially common when your toes get forced upward (toward your body) and your ankle pulls your calf muscles down too quickly.
What happens when you pull your calf?
A pulled calf muscle happens when you overstretch the muscles in the back of your lower leg. It’s a common injury with athletes that do a lot of stop-and-go movements, but it can also affect older, active individuals. Most calf strains heal with rest, ice, compression and elevation. In rare cases, calf muscle tears require surgery.
Can a calf tear cause pain?
A calf strain can cause pain and prevent you from running, jumping and doing other activities. A severely pulled calf muscle can result in partial or complete tears. A torn calf muscle may require surgery. Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission.
How to heal a strained calf muscle?
Reducing pain and symptoms may be achieved by off loading the strained calf musculature through rest, taping techniques, and appropriate soft tissue massage techniques. While somewhat lacking scientific evidence for soft tissue recovery modalities such as dry needling or western acupuncture can be popular amongst runners and may also be useful.
What muscle is the calf muscle?
A calf muscle strain can occur to either of the two primary ‘calf muscles’; the soleus or the gastrocnemius (see anatomy images below): (i) soleus muscle (ii) Gastrocnemius (medial and lateral heads) The muscles at the back of the leg are comprised of a superficial and a deep group of muscles.
Which muscle group is generating high peak forces across all speeds?
Furthermore when looking at peak muscle forces per muscle group across a variety of running speeds it is evident that the soleus muscle is generating high peak forces across all speeds, see image below:
Where does the majority of running force propulsion come from?
Greater than 50% of running force propulsion is generated from ‘below the knee’ plantar flexor musculature. Given the force developed by the calf it is understandable that the calf can be a potential site of muscular injury for a runner.
What are the muscles in the back of the leg?
The muscles at the back of the leg are comprised of a superficial and a deep group of muscles. The superficial group is comprised of: the soleus and gastrocnemius (pictured above) and also the lesser referenced and lesser sized plantaris muscle. The deep group of calf musculature is comprised of: tibialis posterior.
Is high plantar flexor strength protective?
High plantar flexor function seems to be protective against achilles tendinopathy. Willy and Paquette in their review of masters runners state ‘runners with greater eccentric plantarflexor strength and greater propulsive forces during running have a reduced risk of developing achilles tendinopathy (9).
What is the soleus muscle?
The soleus is primarily composed of slow twitch (type 1 muscle fibers) and is the key muscle for endurance running. Runners tend to clump the two superficial muscles together; the soleus and gastrocnemius and collectively refer to these two muscles as the ‘calf’.
How to treat a torn calf muscle?
Once you know that, you'll know how to treat the injury successfully. For minor calf strains, the best approach is rest, ice, compression, and elevation.
How to relieve pain from calf muscle injury?
Wear a heel pad in your shoe for a few days to raise your heel and shorten the injured calf muscle, which will relieve some of the tension / pain. But don't forget about it; if left in place too long can cause a flexion contracture (shortening) of the achilles tendon and permanent stiffness of the ankle.
How to tell between gastrocnemius and soleus strain?
With a more serious strain, it's important to distinguish which muscle is involved to the greater extent: the deeper soleus or the more superficial "heads" of the gastrocnemius. MRI or diagnostic ultrasound may be needed to best diagnose the location and degree of the injury. Grade II strains involve more extensive damage, up to 90% of the muscle fibers may be torn. These injuries present with more pain (described as sharp in nature), significant loss of muscle strength and range of motion. Swelling is more severe and bruising quickly develops because of the internal bleeding from the torn muscle fibers.
Why does my calf hurt?
Furthermore, some serious medical conditions can cause calf pain or refer pain to that region, such as a bone fracture, bone cancer, bone infection (osteomyelitis), venous insufficiency, sciatica from a lumbar disc herniation or complications related to diabetes. [2]
What doctor can help with calf pain?
As such, medical specialists such as an orthopedist (bone and joint specialist), neurologist (nerve specialist) or physiatrist (muscle and bone specialist) may be needed to rule out the most serious causes of your calf pain.
How long does it take for a calf strain to heal?
Most calf strains are minor injuries and self-heal within a week -- the degree of pain, disability and bruising are good indicators of seriousness. Grade I muscle strains involve micro-tears of up to 10% of the muscle fibers.
Which muscle is the lower leg?
The two muscles that work in conjunction to form the lower leg (or calf) are the deeper soleus muscle and the more superficial (closer to the skin) gastrocnemius muscle.
How to get rid of a swollen calf?
Slowly shift your weight to the balls of your feet and use your calf muscles to lift your body weight. Make sure you keep your abdominal muscles tight and do not lean forward. Hold for 30 seconds then return to starting position. Repeat five times with ten seconds rest between sets.
How to strengthen gastrocnemius?
Gastrocnemius (leg) exercises. Standing calf raises are an excellent way to isolate and strengthen gastrocnemius. Stand tall with your feet, knees, hips, and shoulders nicely aligned. Your feet should be about shoulder width apart.
Where does gastrocnemius come from?
The name of gastrocnemius is derived from the Greek words for stomach and leg because the bulging mass of the muscle resembles a “belly of the leg”. Along with the soleus muscle, it comprises the calf muscle group. This powerful muscle runs from the back of the knee all the way down to the heel. It is absolutely essential for locomotion ...
Can ultrasound be used to measure gastrocnemius muscle volume?
Recent trials in rodents have shown great potential for using ultrasound techniques to measure gastrocnemius muscle volume which can be correlated with muscle atrophy. This method is non-invasive and easy to perform and could be significant in assessing muscle atrophy after nerve damage.

The Calf Muscles
Symptoms
- The symptoms of a medial gastrocnemius strain can include:2 1. Decreased flexibility or stiffness 2. Pain in the back of the leg (more on the inner side) 3. Swelling of the calf 4. Bruising of the calf down to the ankle 5. An audible pop or snapping noise at the moment of injury 6. Weakness or a complete lack of function The symptoms of a calf muscle strain depends on the severity of the i…
Causes
- The umbrella term may be "tennis leg," but calf injuries can be caused by virtually any sport, and especially running and soccer.2The gastrocnemius muscle crosses the knee joint and the ankle joint, flexing the foot and the leg. Sudden changes in direction when running can overstretch the muscle and lead to a tear, especially in the position where you are flexing the ankle and extendin…
Diagnosis
- Your healthcare provider will listen to your report of the injury and do a physical examination. A diagnostic ultrasound is the best way to confirm a gastrocnemius tear and grade the injury.3 Other diagnostic tools can help, too. For example, if a deep venous thrombosis (a blood clot in the veins) is suspected, a Doppler ultrasound may be done.4 Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a…
Treatment
- Treatment of a medial gastrocnemius strain can usually be accomplished with simple steps. Initially, patients follow the "RICE" regimen: 1. Rest is vital.Sometimes, people will use crutches for a few days or a week to allow the most significant pain symptoms to subside. 2. Ice on thecalf muscle can ease pain, reduce swelling, and counteract inflamm...
Summary
- A medial gastrocnemius strain leaves little doubt that something serious has happened. A sudden, lurching or pulling movement can cause sharp pain, swelling, bruising, or weakness in the lower leg. The strain is often referred to as "tennis leg," though it can happen while playing other sports or undertaking physical activities, especially running. You might even hear a popping or s…
A Word from Verywell
- Tennis leg is most common among middle-aged people, presumably because their muscles are often just starting to weaken and so are more vulnerable to injury. Even if you don't play tennis, you don't want to experience tennis leg. It can be surprisingly painful. And if you do play tennis, then you might guess that the best "treatment" of all is prevention. So be sure to warm up befor…