Explore
May 31, 2018 · Decreased or limited motion Treatment The treatment of ulnar wrist pain depends on the diagnosis. It can include some combination of activity modification, splinting or casting, hand therapy, anti-inflammatory medicine and/or steroid injections. If non-operative treatment does not relieve symptoms, surgery might be considered.
What is the treatment for ulnar wrist pain?
• Tolerance to light/unloaded daily activities without increase in pain • 70% strength of contralateral side PHASE III: LATE/CHRONIC (4-6+ WEEKS) Rehabilitation Goals • Maintain full ROM • Promote proper movement patterns • Avoid post-exercise pain/swelling Additional Interventions *Continue with Phase I-II Interventions
What to do if your wrist Hurts when you extend it?
Physical therapy (exercises to mobilize, strengthen tendons and ligaments in the wrist) Casting or splinting to rest the wrist Surgery to remove a growth or other cause of nerve compression, repair tendon or ligament tears, fix fractures or treat arthritis through open or arthroscopic surgery including forms of joint replacement
How do you treat a torn ligament in your wrist?
Aug 10, 2020 · Your hand surgeon may treat your pain with a variety of methods (both non-surgical and surgical), depending on your condition. Your doctor will examine your wrist and potentially take x-rays to determine the cause of pain. Treatment options can include activity modification, splints, therapy, medicine or surgery.
What is the post-surgical treatment for wrist and thumb tendonitis?
Mar 21, 2022 · Both medial and lateral epicondylitis were historically classified as inflammatory disorders, resulting in conservative pain management with anti-inflammatory drug administration, physical therapy, rest, and steroid injections with variable long-term success.3 The scar tissue formation provoked by conservative management creates a tendon lacking the biomechanical …
How do you fix ulnar sided wrist pain?
What are conservative treatments for ulnar sided wrist pain?Rest to allow for self-healing.Activity modification to reduce and redirect repetitive motions.Casting or splinting for broken bones.Anti-inflammatory medications.Steroid injections.Physical therapy.
How do you fix outer wrist pain?
How is ulnar wrist pain managed or treated?Taking anti-inflammatory medication, such as naproxen or ibuprofen or newer non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDS), or steroid injections to ease pain.Changing your hand's position during repetitive motions (ergonomic adjustment)More items...•Feb 26, 2019
How do you rehabilitate wrist tendonitis?
ExercisesWrist Tendonitis Rehabilitation ExercisesFlexion: Gently bend your wrist forward. Hold for 5 seconds. Do 3 sets of 10. ... Extension: Gently bend your wrist backward. Hold this position 5 seconds. ... Side to side: Gently move your wrist from side to side (a handshake motion). Hold for 5 seconds at each end.
How do you strengthen tendons and ligaments in the wrist?
Wrist extensor stretch Extend the arm with the affected wrist in front of you and point your fingers toward the floor. With your other hand, gently bend your wrist farther until you feel a mild to moderate stretch in your forearm. Hold the stretch for at least 15 to 30 seconds. Repeat 2 to 4 times.
How do you strengthen your outer wrist?
Hold a weight with your palms facing down and your wrist hanging over the knee. Move your hand up as far as possible and then down as far as possible in a slow and controlled motion. Do a set of 10, then repeat. Repeat the exercise, but with your palms facing up.Jul 8, 2019
Should I workout with wrist pain?
Do not suffer or continue to exercise with pain. Hand and wrist pain can make it difficult to do even simple everyday tasks, leisure activities and work. A Hand Therapist can help to assess any possible causes for wrist pain and tell you why your hand might be hurting.
Can I lift weights with wrist tendonitis?
In severe cases of tendinopathy, the tendon can rupture or tear. If you have a tendinopathy affecting your elbow or wrist, you can still use the muscles in your lower body to get a good workout and maintain your fitness level.Jan 10, 2019
What is the fastest way to heal tendonitis in the wrist?
Splints to rest the thumb and wrist. Changing activities to avoid doing anything that might cause pain. Ice or a cold compress to cut inflammation and pain....MedicationsNonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) to help relieve the swelling and pain. ... Corticosteroid injections into the tendon sheath.More items...•Feb 4, 2021
Is yoga good for tendonitis?
But you can still do yoga with tendonitis, and it can, in fact, help to relieve the symptoms and prevent it from occurring. Often, mild tendonitis will heal itself, but there are some simple yoga exercises you can do to encourage this process.
What helps ligaments heal faster?
The high concentration of platelets helps your ligament heal faster than it normally would.
What foods help repair ligaments?
These nutrients have all been shown to support and repair ligaments, tendons, and discs.Manganese – nuts, legumes, seeds, whole grains, leafy green veggies.Omega-3 – as listed above, salmon, mackerel, etc.Vitamin A – liver, carrots, sweet potato, kale, spinach, apricots, broccoli, winter squash.More items...
Does vitamin C help heal ligaments?
Vitamin C – also known as ascorbic acid, is a key vitamin for ligament repair and collagen production. It is recommended to increase your intake of vitamin C immediately after an injury to help support the healing process as it directly assists in wound healing and tissue repair.Dec 1, 2014
What is the most common sprain in the wrist?
Most common: Posterior interosseous/radial nerve entrapment. Ganglion cyst – a ganglion cyst or wrist ganglion is a small lump that appears in the wrist and is often attached to a ligament. Scapholunate ligament sprain – wrist sprain affecting the ligament between the scaphoid bone and lunate bones. Less common:
What is the dorsal radial zone?
The dorsal radial zone is the area of the wrist near the thumb over the palm side. Most common: Extensor carpi radialis tenosynovitis – inflammation of the sheath surrounding the tendon. DeQuervain’s tenosynovitis – inflammation of the sheath that surrounds two tendons in the wrist at the base of the thumb. Scaphoid fracture – a fracture ...
What is a scaphoid fracture?
Scaphoid fracture – a fracture to the carpal bone in the wrist called the Scaphoid. Distal radius fracture (Colles fracture) – a fracture of the end of the radius bone in the forearm. Carpal dislocation – dislocation of any of the small bones which make up the wrist.
Who is Mike Walden?
Mike Walden. Mike is creator & CEO of Sportsinjuryclinic.net. A qualified Sports Injury Therapist with a degree in Physical Education, Sports Science and Physics, and a Postgraduate Certificate in Education.
How to treat ulnar wrist pain?
Standard treatments to relieve pain include: Taking anti-inflammatory medication, such as naproxen or ibuprofen or newer non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDS), or steroid injections to ease pain.
What is a broken wrist?
Fractures. Broken wrist or hand bones, or the end result of old fractures involving the ulnar styloid, hook of hamate or pisiform bones. Nerve injuries or compression. Damage to or pressure on nerves in the wrist, or higher in the arm or neck, resulting in irritation of the ulnar nerve. Overuse.
What does it mean when your wrist is clicking?
Popping or clicking noise in your wrist associated with sharp pain with movement. Loss of strength in the hand when gripping strongly, associated with pain. Loss of movement at the wrist especially with rotation of the forearm and with lateral movement of the wrist towards the pinky side (ulnar deviation)
What causes a wrist joint to swell?
Arthritis. Inflammation (swelling) and stiffness in the wrist joint. This may include osteoarthritis (wear and tear of the cartilage of bones in the wrist joint), inflammatory arthritis, such as rheumatoid arthritis, or arthritis due to crystal deposits in the joint from gout or pseudo-gout. Fractures.
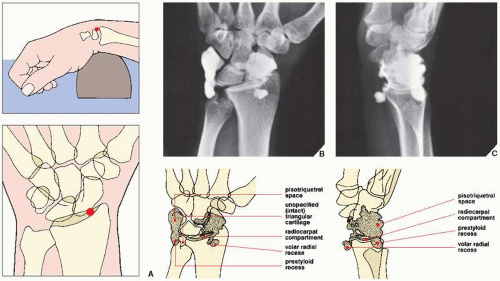
What is TFCC injury?
Overuse. Damaged tendons and ligaments due to repeated hand and arm motions or injuries. Triangular fibrocartilage complex (TFCC) injury. Tears or fraying in the tissues that connect the ulna to other parts of the wrist, often from a fall onto the wrist, or multiple repetitive twisting injuries.
What is the purpose of ultrasound in wrist?
Ultrasound to identify foreign bodies in the wrist area, tendon ruptures, tendinitis, compressed nerves, check blood flow, assess abnormal growths. Wrist arthrography uses a radiopaque fluid injected into the joint to enhance view of the joint structures before performing many of the above imaging studies.
What is the Cleveland Clinic?
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center.
How to treat a swollen wrist?
Your hand surgeon may treat your pain with a variety of methods (both non-surgical and surgical), depending on your condition. Your doctor will examine your wrist and potentially take x-rays to determine the cause of pain. Treatment options can include activity modification, splints, therapy, medicine or surgery.
What causes wrist pain?
Arthritis. There are many different types of arthritis that can affect the hands and wrists. Arthritis in general can cause pain and stiffness. If you’re experiencing wrist pain, you may be suffering from a type of arthritis such as rheumatoid arthritis or osteoarthri tis. Ulnar Impaction Syndrome.
How to tell if your wrist is hurting?
Wrist pain can come in many forms. In addition to regular pain on the pinkie side of your wrist, you may also feel: 1 A clicking or popping sound when you move your wrist 2 Decreased grip strength 3 Inability to fully move your wrist like normal
Why does my wrist make a clicking sound?
A clicking or popping sound when you move your wrist. Inability to fully move your wrist like normal. Some potential causes of ulnar-sided wrist pain include: Regardless of how severe or moderate your wrist pain is, there’s a chance you have a wrist fracture, which is another name for a broken wrist.
What causes numbness in the wrist?
Neve Injury. Nerves can be damaged by too much pressure, by stretching, or by something as simple as a cut, causing pain, numbness or weakness in the wrist or hand. If you’re experiencing ulnar wrist pain, it’s important to visit a hand surgeon as soon as possible.
What is the TFCC?
The TFCC (the triangular fibrocartilage complex) is an important structure that helps connect the forearm with the small bones in the ulnar side of the wrist. It can tear from natural wear or from an injury and may be the cause of your wrist pain.
What is the pain of the first dorsal compartment?
Patients with DeQuervain’s tenosynovitis commonly present with pain over the first dorsal compartment, especially with thumb flexion and ulnar deviation (also known as Finkelstein’s test ). The first dorsal compartment consists of two tendons – extensor pollicis brevis (EPB) and abductor pollicis longus (APL).
What is a thumb spica?
forearm-based thumb spica (positioned with thumb midway between palmar and radial abduction and able to oppose the small finger) worn full-time and only removed for hygiene and gentle wrist/thumb AROM daily.
What is CMC osteoarthritis?
CMC osteoarthritis, also commonly called basilar joint arthritis or CMC degenerative joint disease, is essentially “wear and tear” of the trapezi um and base of first metacarpal (Cannon, 2001, p. 8). Patients commonly report localized pain at the base of the thumb, which increases with activity.
How much resistance is required for isometrics?
Isometrics – within pain-free ranges, 50% resistance with 3-5 second holds. In my experience, it is important to thoroughly educate patients on the appropriate way to complete isometrics as it is very common for patients to apply too much resistance and actually cause further damage.
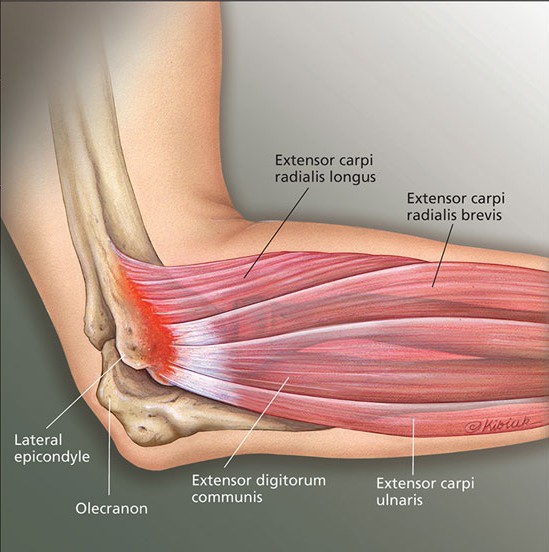
Is medial epicondylitis a difficult diagnosis?
Lateral or medial epicondylitis (epicondylosis) can be a very challenging diagnosis to treat, as there are varying opinions on best treatment practices. Patients present with palpable pain over the lateral epicondyle due to micro/macroscopic tears within the fiber origin of the common extensor mass, primarily involving the extensor carpi radialis brevis (ECRB) and secondarily the extensor digitorum communis (EDC) or extensor carpi radialis longus (ECRL) (Cannon, 2001, p. 224).
