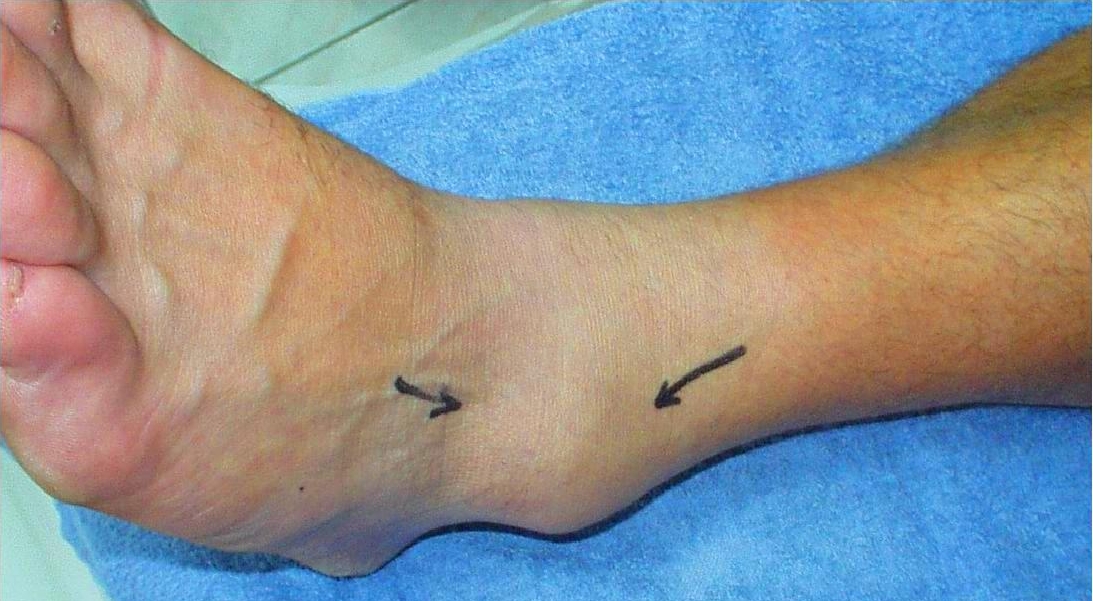
Rest, time, and physical therapy. Because this area of the back is sensitive, it’s essential to make sure that the young athlete works with a physical therapy professional, who will help the patient learn and execute any exercises they do to relieve pain.
Full Answer
What kind of care do young athletes need?
Rehabilitation of a Young Athlete With Extension-Based Low Back Pain Addressing Motor-Control Impairments and Central Sensitization. Activity modification, bracing, and traditional core-strengthening exercises may not be the most appropriate treatment for athletes experiencing EB LBP. Addressing cognitive-affective factors in addition to correcting maladaptive motor …
What's new at the young athlete center?
Feb 01, 2018 · Low back pain (LBP) is estimated to occur in 10% to 15% of young athletes, but the prevalence in some sports that require repetitive lumbar extension may be higher. 1 The condition occurs frequently in artistic gymnasts (50%) and rhythmic gymnasts (86%). 2,3 Approximately half of the young athletes who present with extension-based (EB) LBP have a fracture in the pars …
How are athletes treated for substance addiction?
Dec 20, 2021 · When it comes to treating athletes who are struggling with substance addiction, certain elements of generally accepted methods of healing apply; other forms of therapy are unique to the sporting world. Individual circumstances will determine the first stages of treatment, which will usually involve a period of medical detoxification. This will ensure that the athlete’s …
Why is it important for young athletes to play sports?
Abstract. Early specialisation in sports continues to increase and is a risk factor for the incidence of injuries in young athletes. In overhead athletes, the shoulder is the most affected joint, related to a combination of impingement and glenohumeral instability, as well as musculoskeletal immaturity. Identification of risk factors and rehabilitation is usually an effective recovery …
How do young athletes recover?
After an intense practice or game, consume a snack that is a mixture of protein, carbohydrates, and fats. The meal following your snack should be rich in nutrient dense carbohydrates, like multi-grain bread, brown rice, vegetables and fruit, and should also contain high quality protein to help you rebuild muscles.
What is the best way for an athlete to recover?
8 best recovery techniques for athletes to turn into habits:The RICE Method - Rest. Ice. ... Active recovery. One of the best ways to heal quickly is through active recovery. ... Stretching. ... Self-Myofascial Release & Foam Rolling. ... Refueling. ... Meditation / Yoga. ... Implementing Healthy Lifestyle Habits. ... Rest.
How soon can an athlete start rehabilitation?
The process of rehabilitation should start as early as possible after an injury and form a continuum with other therapeutic interventions. It can also start before or immediately after surgery when an injury requires a surgical intervention.
How do you cheer up an injured athlete?
Demonstrate empathy towards your injured athlete. Tell them that you understand how hard this is on them and make it clear that you will help them through it. Continue to be a “Coach.” Do what you've always done for your athletes. Encourage and inspire the injured athlete.
How do elite athletes recover?
Recovery is becoming increasingly important to the high-performing athlete in a bid to reduce fatigue and enhance performance. Some of the more common recovery techniques utilised by athletes include hydrotherapy, active recovery, stretching, compression garments and massage.
How do pro athletes recover so quickly?
Granted, some professional athletes speed their return to competition by overusing painkillers, anti-inflammatories and other prescription drugs and by succumbing to pressure from teams to play through injuries, as The Washington Post reported in a series of stories last spring.Nov 11, 2013
What are the 5 stages of rehab?
Don't Forget the RehabPhase 1 - Control Pain and Swelling.Phase 2 - Improve Range of Motion and/or Flexibility.Phase 3 - Improve Strength & Begin Proprioception/Balance Training.Phase 4 - Proprioception/Balance Training & Sport-Specific Training.Phase 5 - Gradual Return to Full Activity.
What are the three phases of rehab?
Athletic trainers (ATs) have traditionally conceptualized rehabilitation programs in terms of 3 distinct physiologic phases: acute injury phase, repair phase, and remodeling phase.
What are the 7 principles of rehabilitation?
7 Principles of Sports Rehabilitation Avoid aggravation. It is important not to aggravate the injury during the rehabilitation process. ... Timing. ... Compliance. ... Individualization. ... Specific sequencing. ... Intensity. ... Total patient.
How do I overcome my fear of sports injuries?
Fear of injuryLearn how to warm up and cool down to prevent injury.Learn how to exercise appropriately considering your age, fitness level, skill level, and health status.Choose activities you feel you can do safely, and increase the amount you do gradually as your confidence and abilities grow.
What should athletes do when injured?
So what should athletes do? First, stop playing as soon as you notice an injury and talk to your coach or doctor. Then keep resting until you are fully healed and your doctor gives the go ahead (even if you feel sort of OK and there's a big game coming up, don't play unless your doctor says you can).
How injury affects athletes psychologically?
In these athletes, an injury may result in even greater emotional upheaval. Emotional responses to injury include sadness, feelings of isolation, irritation, lack of motivation, frustration, anger, alterations in appetite, sleep disturbance, and feeling disengaged.
Why do young athletes have EB LBP?
When young athletes continue to experience EB LBP, impaired motor control, as opposed to muscle weakness alone , may be the reason. Central sensitization of pain must also be considered as a result of sustained peripheral nociceptive input resulting in changes at the spinal cord and cortical levels combined with maladaptive cognitive-affective factors. 24 Atrophy and fatty infiltrate of the LMM can compromise neuromuscular function and contribute to dysfunctional movement patterns that place a greater demand on lumbar spine structures. 22 Strengthening a muscle alone does not ensure that an athlete will use a muscle when needed to perform an activity. 35
Why did the athlete have difficulty controlling trunk extension during sport-specific activities?
The athlete had difficulty controlling trunk extension during sport-specific activities; she moved early and to a greater extent in the lumbar spine. The aim of the treatment was to teach the athlete how to control her tendency to overload her lumbar spine when bending backward, thus reducing nociceptive input from lumbar spine structures and desensitizing the nervous system.
How long did a 15 year old female gymnast have EB?
The 15-year-old female gymnast had a 4-year history of episodic EB LBP. She described her pain as a deep ache in her low back and rated it at 0/10 at best, 3/10 at the time of the evaluation, and 6/10 at worst. Over 4 years, she had undergone several courses of outpatient orthopaedic rehabilitation that focused on core muscle strengthening but had no long-lasting improvement. Although the pars interarticularis fracture was healed, the athlete referred to her LBP as “the fracture in my back.” She was unable to tolerate higher levels of gymnastic training or competition. At the time of the evaluation, she was unable to practice at all. The athlete's goal was to return to competitive gymnastics.
How can sports psychologists help athletes?
The American Psychological Association explains that in ideal circumstances, sports psychologists can help athletes improve their performances through various mental strategies, boost their motivation, and rediscover a passion for their sport when the novelty wears off.
Why do athletes turn to drugs?
Various aspects of athletic life are conducive to drug abuse; in addition to performance enhancement, athletes take drugs (or are given drugs to take) to medicate injuries, and to deal with mental and emotional stress that comes from life on and off the field, track, court, or ring, and even after retirement. Consuming these drugs (especially in a high-pressure and high-risk environment, like professional sports and athletics) presents a significant risk of developing an addiction to them.
What injuries did Earl Campbell have?
Earl Campbell was one of the greatest college football players in history, but par-for-the-course injuries made the spinal stenosis he was born with even worse. Campbell washed down his prescriptions of Vicodin and OxyContin with Budweiser, later calling his battle with addiction his “toughest opponent.”.
What is sports psychology?
Sports Psychology. Athletes are driven to succeed in ways that people in other vocations rarely are. Athletic competitions, especially those in the professional sporting world, combine arenas of mental and physical toughness, but also the pressure of a rabid consumer market, as well as coaches and families who have invested a lifetime’s worth ...
Does detoxing help with addiction?
The National Institute on Drug Abuse writes that medical detox alone does little to correct addictive behavior in the long run. For that, an athlete would need counseling and therapy to address the mental damage done by the addiction.
How many square feet is the Young Athlete Center?
Young athletes requiring rehabilitation now have a space designed just for them. The Young Athlete Center's new 4,000-square-foot therapy and injury prevention space for sport-specific rehab accommodates running, jumping, kicking and throwing. The space includes:
What is the Washington University sports medicine team?
Louis Children’s Young Athlete Center is dedicated to caring for kids of all ages with sports-related injuries .
Why is sports important for young people?
For young athletes, regular participation in sports can provide numerous psychological and social advantages, as well as improvements in overall health and fitness ( 3,6,11 ). If children and adolescents continue to play and have fun, they can enjoy the myriad benefits of healthy sports participation for a lifetime.
Why is youth sports so exclusionary?
The youth sports industry has become exclusionary, as the professional model of development increasingly is prevalent and accepted. Youth who follow this model often cannot keep up with the unrealistic expectations and excessive demands. Too much play, training, travel, and pressure frequently lead to a variety of physical ...
What happens after musculoskeletal injury?
Further, after a serious musculoskeletal injury, a young athlete's risk of incurring subsequent related injuries often is the same or greater when rehabilitation is minimized and incomplete or the contributing factors related to technique, fitness, training, and preparation/recovery are not corrected.
Why are youth sports important?
Youth sports provide numerous health-enhancing and other important benefits to participating children and adolescents. However, the motivations and goals of young athletes often conflict with those of adult stakeholders, and they are redirected. The youth sports industry has become exclusionary, as the professional model of development increasingly is prevalent and accepted. Youth who follow this model often cannot keep up with the unrealistic expectations and excessive demands. Too much play, training, travel, and pressure frequently lead to a variety of physical and psychological problems, particularly concurrent with the vulnerability of a young athlete going through pre- or early adolescence and the rapid growth phase. The need for alternative models, emphasizing fun and fundamentals, is becoming increasingly clear and urgent. With appropriate changes, youth sports once again can be an effective entry point for a lifetime of healthy sports participation and enjoyment.
Is there evidence of similarly motivated changes in athlete development in the United States?
Noticeably, there is prominent evidence of similarly motivated changes in athlete development in the United States, as well. Certain sport governing bodies have been making appreciable changes in access for youth and more appropriate early entry into their sports, with a principal focus on health and fun.
Do adults determine a young athlete's potential?
Unfortunately, too often adults determine a young athlete's potential, emphasis on a specialized sports "career," and success (or not) well before adolescence, and the adult stakeholders divert the youth's natural enthusiasm.
Is single sport evidence based?
Malina additionally notes that youth single-sport development models and programs are not sufficiently evidence-based, despite recognized, albeit invalid, perceptions of success. There also are numerous examples of prevalent related risks - overuse injury, social isolation, and burnout, to name a few.
