
What are the benefits of soleus exercise?
Nov 17, 2021 · Unlike the gastrocnemius, the soleus only crosses the ankle and is largely comprised of type 1 slow twitch muscle fibers (1), meaning that the soleus is fairly resistant against fatigue. Although the soleus does have its own separate and anatomically distinct origin, it actually blends into the Achilles tendon with the gastrocnemius. Another ...
How can I strengthen my soleus?
Nov 27, 2014 · The soleus (L. solea, sandal.) is the smaller of the two major calf muscles; the other muscle being the gastrocnemius (gastroc). Fun fact: It was originally named after its resemblance to the flat, sandal-shaped sole fish, whose name also comes from the Latin word, solea. The soleus and gastroc are both prime movers in ankle plantarflexion when ...
What are the treatments for a soleus injury?
Sep 08, 2021 · I know I bang on A LOT about how important the quads are for ACL rehab (and this won't change anytime soon), but another muscle we need to make sure we don't overlook in ACL injury prevention & rehab is the soleus! Maniar et al (2020) published data on muscle activity contributing to shear & rotational forces across the knee joint during single leg landing.
How do you work the soleus muscle in your knees?
Jun 11, 2019 · Hold a set of weights and rest them on your knee for added resistance. Lower and raise your heel for 10 to 15 repetitions. Resistance bands also allow you to add additional resistance to strengthen the soleus muscle. Begin seated on a mat with both legs straight in front of you. Wrap a resistance band around the balls of your fee.
Which muscle is the soleus?
The soleus is a fairly under-appreciated muscle next to its larger neighbor, the gastrocnemius. It holds some value from a clinical and performance perspective, but focusing on the gastroc likely will provide more yield.
What muscle fibers are in the soleus?
Unlike the gastrocnemius, the soleus only crosses the ankle and is largely comprised of type 1 slow twitch muscle fibers (1), meaning that the soleus is fairly resistant against fatigue. Although the soleus does have its own separate and anatomically distinct origin, it actually blends into the Achilles tendon with the gastrocnemius.
What muscle is the third muscle of the triceps surae?
Lastly, if the soleus is the step-child that never got the recognition it deserved next to the gastroc, the plantaris (the third muscle of the triceps surae) is the distant cousin that the family shunned to live in the backyard shed. Poor plantaris.
What is the calf called?
Due to the unique anatomy of these three muscles, the calf is often referred to as the triceps surae in the medical / rehabilitative literature. The action of the soleus is to create plantar flexion (pointing the foot down). It serves a particularly important role in standing, walking and running.
Where does the soleus originate?
In technical terms, it originates from the soleal line/medial border of the tibia, head of the fibula and the posterior border of the fibula.
Which tendon has the longest function?
In comparison to the plantaris, the soleus certainly holds more function. However, if looking for some physical therapy trivia, the plantaris is said to be the longest tendon in the body.
What is an Achilles rehab program?
The Achilles [P]Rehab Program is the ultimate resource for those looking to strengthen, protect, and optimize their achilles tendon. This program is designed for active individuals looking to improve their performance that may be dealing with an Achilles weak link. With this 3-phase program, you will build up your Achilles tendon to handle anything life throws at you! Learn more HERE!
What is the soleus muscle?
It’s also worth noting that the soleus is an important ankle stabilizer, which allows us to stand upright. Without it, we’d fall on our faces. Note: While the soleus and the gastrocnemius are separate muscles, they are often referred to collectively as the “triceps surae” which means “three-headed muscle of the calf” (the soleus has one head, ...
What is the soleus?
Soleus: Functional Anatomy Guide. The soleus (L. solea, sandal.) is the smaller of the two major calf muscles ; the other muscle being the gastrocnemius (gastroc). Fun fact: It was originally named after its resemblance to the flat, sandal-shaped sole fish, whose name also comes from the Latin word, solea. The soleus and gastroc are both prime ...
What muscles do you stretch when your plantarflexors are overactive?
Release and stretch the soleus and gastrocnemius. When the plantarflexors are overactive/short, the dorsiflexors become inhibited/long and need to be strengthened. To do this, add reverse calf raises to your training.
What is the short soleus?
Overactive/Short Soleus: The soleus is overactive and short in individuals with lower crossed syndrome (LCS) and/or pronation distortion syndrome (PDS). In LCS, the soleus compensates for poor hip extension due to weak glutes during the gait cycle by becoming overactive to produce excessive plantarflexion.
Why is my soleus short?
The knee adduction and foot pronation associated with PDS puts more stress on the soleus. Also, the soleus can become overactive/short via overuse from doing activities that involve a lot of plantarflexion (e.g. running, a job that requires lots of standing or walking).
What to do if you have lower cross syndrome?
If you also have lower cross syndrome, you must take care of the other issues causing it. This includes strengthening your glutes and abs / obliques, in addition to stretching and releasing your hip flexors and lower spinal erectors. See how to fix lower cross syndrome (article coming soon) for more details.
Where is the soleus located?
Classified as part of the superficial posterior compartment of the leg, the soleus is located deep to the gastroc. Most of its mass is invisible from the surface of the physique. However, when developed, it is clearly visible on either side of the gastroc and on the lower part of the calf. The soleus originates from different points in or ...
How to strengthen soleus muscle?
Slowly lower the heel until the ankle is fully flexed. Then raise up onto your toes, keeping the knee straight. You can perform this exercise with both legs or one leg at a time. This exercise not only strengthens your soleus but it also works the gastrocnemius muscle and increases the range of motion in your ankle.
How to do soleus exercises?
One of the basic soleus exercises is calf raises, or standing heel raises, according to the American Council on Exercise. Begin this exercise with the ball of your foot on a step with your heel hanging over the edge. Slowly lower the heel until the ankle is fully flexed.
How to stretch gastrocnemius muscle?
To isolate the stretch to the soleus muscle, simply bend the back knee during the stretch, keeping the heel planted on the ground. Hold the stretch for 15 to 30 seconds and repeat two to four times on each leg.
How to work soleus and gastrocnemius?
Begin seated on a mat with both legs straight in front of you. Wrap a resistance band around the balls of your fee. Keeping the band taught and your knees straight, flex your toes back toward your body as far as you can, then point your toes to work both the soleus and gastrocnemius.
What muscle does the soleus work?
Calf raises work the soleus muscle. Image Credit: kali9/E+/GettyImages. Soleus exercises strengthen your calf and help prevent injuries. The soleus muscle is one of two muscles in your calf. The other is the gastrocnemius muscle.
How to get rid of a swollen calf?
Cool down after your workout with five to 10 minutes of walking or biking at an easy pace. Finish by stretching your calf muscles. Try the wall stretching exercise described by the American Council on Exercise. Stand one arm's length away from the wall and place your palms on the wall just below shoulder height.
How to work soleus?
There are several options to work your soleus using bands or weights. For example, try a seated heel raise with weights. This move is done with your knees bent, which deactivates the gastrocnemius, allowing the soleus to bear the load. Begin sitting with the balls of your feet on a step in front of you .
What muscles do calf raises strengthen?
There are lots of variations of the seated calf raise, all of which will strengthen the soleus muscles of your lower legs . The key is to work through a full range of motion. If playback doesn't begin shortly, try restarting your device.
What muscle is injured in the calf?
These injured runners often test as having a significant strength imbalance, between gastrocnemius, the biggest of and most superficial of the calf muscles, and soleus which sits deeper and lower in the calf region. Here’s a quick visual aid:
How many reps should I do for a calf raise?
Aim for 3 sets of 15 rep s on each leg. If you have a gym available, you might also want to try incorporating seated calf raises into your calf strengthening programme. There are lots of variations of the seated calf raise, all of which will strengthen the soleus muscles of your lower legs.
How to stretch soleus?
Stand with your heels hanging over the back of a step, with your toes on the step. Hold onto something stable for support, if required. Drop your heel s downwards. You should feel a stretch up the back of your calfs. Perform the exercise anytime the legs tighten up.
What is the soleus muscle?
The soleus muscle is one of the powerful plantar flexor muscles in the ankle joint. It receives its blood supply from a number of different sources. A study was conducted to describe the distribution of the arterial supply for blood to the soleus muscle. The soleus muscle is supplied by perforators of the popliteal, posterior tibial and peroneal arteries. They found that the posterior tibial artery gave 38.8% of total perforators, while the peroneal artery gave 33.3% and the popliteal artery gave 27.8%. The study concluded that as it is richly supplied with arterial blood, the soleus can be used safely as a free flap, hemisoleus flap or composite flap to cover defects in the lower limb.
Where does the blood supply to the distal muscle come from?
Blood supply. Proximal to distal muscle is supplied from the sural branches of the popliteal artery, peroneal artery and posterior tibial artery. Tendons receive blood from the posterior and anterior, lateral and medial malleolar arteries, lateral plantar artery and calcanean branches in the posterior tibial artery.
Which arteries supply the soleus muscle?
The soleus muscle is supplied by perforators of the popliteal, posterior tibial and peroneal arteries. They found that the posterior tibial artery gave 38.8% of total perforators, while the peroneal artery gave 33.3% and the popliteal artery gave 27.8%.
What is the best treatment for soleus?
Cryotherapy is often used to treat the muscle, which uses a low temperature to help cool the body parts down. Ultrasound therapy and passive stretching are two other types of treatments for soleus injuries. After therapy, strength training is often advised.
How to stretch your legs at the same time?
Stand about a foot away from the wall with the back straight and the palms pressed to the wall. Lean gently toward the wall while bending the knees to form a shallow squatting position . Keep both heels firmly on the floor while holding onto the stretch. The stretch allows you to stretch both legs at the same time.
Where is the soleus located?
The Soleus is one of the powerful muscles located in the back part of the calf. It runs from just beneath the knee all the way down to the heel. Due to its close connection with the gastrocnemius, some anatomists consider them to be a single muscle called the triceps surae. It is used for walking and standing.
What type of muscle is the soleus?
These fibers power the explosive moves required in sprinting. In contrast, the soleus is a deeper muscle and is made up of more Type I endurance fibers.
How to stretch the soleus of the left leg?
The gastrocnemius of the left leg should feel a significant stretch. After 30 seconds, bend the left knee to shift stretch to the soleus. After holding the stretch for 30 seconds, switch legs.
What muscles are responsible for plantar flexion?
The soleus is one of the three powerful muscles of the calf that lies behind the gastrocnemius, and runs from the Achilles tendon to behind and just below the knee. “The soleus is responsible for plantar flexion, which is when your toes point downward,” explains Tom Holland, an exercise physiologist, sports nutritionist, and coach.
How to tell if soleus is strained?
The classic symptoms indicating a soleus strain are tightness in the entire calf muscle, stiffness, and pain that increases in intensity over several days or weeks. Swelling is typically mild; however, even the simple movements of walking and jogging will likely provoke and exacerbate the symptoms.
Which muscle is used to stretch the Achilles tendon?
Here the tension switches from the gastrocnemius muscle to the Achilles tendon and soleus of the left leg. Repeat the stretch on the other leg. Another simple and often-performed movement is the stair stretch.
What is the soleus?
Soleus: The Shock Absorber. We have all had the experience of acute muscle soreness, especially if you’ve ever began a running program. When the soleus muscle is tight or lacks strength, blood flow to the foot and ankle can be interrupted.
Which muscle is made up of more Type I endurance fibers?
In contrast, the soleus is a deeper muscle and is made up of more Type I endurance fibers. These are the fibers our bodies call upon when moving great distances, such as running a marathon. In addition, the gastroc is only powerful when the knee is straight.
How to get rid of soleus muscle strain?
Overstretch the muscle to the point where you feel pain. Bounce in any of the poses. Stretch cold muscles since it can do more harm. Soleus muscle strain recovery can take time, and it can mean that you have to give up some of your regular activities temporarily, including sports.
How to get rid of a sore soleus muscle?
The next step is to rise up onto the balls of the feet several times while keeping the knees bent. If you feel discomfort or pain, it could be a soleus muscle strain.
How to get your toes to go straight in the air?
Lie on your back with one leg extended while the other knee is bent with the foot flat on the floor. Place a towel under the toes of the bent leg and pull up so your leg is straight in the air. Pull on the towel to pull your toes toward your body as you use your soleus muscle to push your heel toward the ceiling.
What muscle is responsible for the Achilles tendon?
The soleus muscle is what helps form the Achilles tendon. Aside from being an important muscle for walking and running, the soleus helps circulate blood by returning it to the heart. Soleus muscle strain or injury can make it very difficult to perform daily tasks and recreational activities.
What are the symptoms of soleus pain?
A list of common soleus pain symptoms is listed below. Pain in the calf that radiates to the back of the knee. Severe pain in the ankle that makes it hard to bear weight. Severe knee pain. Low back pain. Sensitivity in the lower back area. Circulation problems in the affected foot.
What is the best treatment for soleus pain?
Wraps: These are used to compress the affected area, helping with swelling and pain relief. Active Release Technique (ART): This is a hands-on technique to treat muscle, ligament, fascia, tendon, nerve, or capsule pain. In the case of soleus pain, the muscle is held with tension applied to the tissue.
Why does my soleus hurt?
Soleus pain causes are often linked to certain activities, but there is one cause that you could say is due to inactivity. Check out the list of soleus muscle pain causes below to see what we mean. Walking on inclines, such as hills. Frequent stair climbing. Frequent cycling.
How long does it take for a soleus muscle to heal?
Friction therapy coupled with massage can help speed the process along, enabling the healing of recent injuries within four to six weeks and more long-standing injuries within eight to 12 weeks. To perform fiction therapy on the soleus muscle, have the client lie face down on your table.
How to test for soleus muscle strain?
Ask the person to bend the knees as far as possible, keeping the heels firmly on the floor and the back erect. Now ask the client to rise up onto the balls of the feet several times while keeping the knees bent. If the soleus muscle is severely strained, this will cause discomfort or pain. Test 2.
What is the largest muscle in the calf?
The soleus (Image 1) is the largest and strongest muscle in the calf. It gains its power from its complex configuration, attaching to its corresponding tendons at a 45-degree slant (called a multi-pennate structure) in multiple rows. The muscle starts at the top of the calf and attaches to the Achilles tendon at the bottom.
What does it mean when your soleus is injured?
Injury Verification. When the soleus is injured, a dull aching pain begins during, or directly after, strenuous activity . This injury isn’t usually debilitating, but it puts a stop to the strenuous activities a person might enjoy doing, like tennis, biking, or running.
Why does running uphill strain the soleus?
As mentioned, running uphill is one way people strain the soleus. That’s because running uphill forces a person to bend his or her knees more than usual , and that puts a lot more stress on the soleus muscle. This same kind of stress is experienced with a lot of high jumping. Most people don’t roll through the foot when they land from a jump, ...
Where is the pain from a soleus strain?
Image 1: Soleus muscle. Pain from a soleus strain is felt deep in the calf, usually in the superior part, toward the knee. Discomfort can be felt in one spot or over a broad area, because this injury can leave many fibers strained and inflamed.
How to increase stress on injured leg?
Have the client stand on one leg (the injured one), holding onto something for balance. Now have the person rise onto the ball of the foot, being sure to keep the knee bent.

The Presentation
- A runner comes into the clinic and complains of sharp pain or intense tightening low down in the calf, but above the Achilles. The history is typically as follows: 1. Training for an event; 2. Increased distance or added hill work; 3. A little tight for a week or so; 4. With further training, sy…
Anatomy and Physiology
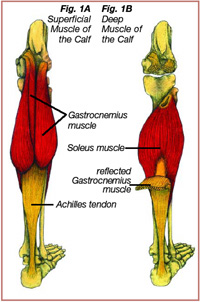
- The soleus is an ankle plantar flexor that originates from the posterior surface of the proximal fibula and the soleal line or medial border of the tibial shaft (see figure 1). It joins the calcaneal, or Achilles, tendon along with gastrocnemius muscles to insert into the posterior aspect of the calcaneus. Its plantar flexion action over the ankle is accentuated when the knee is bent and the …
Figure 1: Calf Anatomy
- Important distinctions between the soleus and gastrocnemius muscles are that the soleus is mono-articular and the gastrocnemius muscle is bi-articular. The soleus has a high proportion of slow twitch muscle fibers and gastrocnemius muscle a high proportion of fast twitch(1). For moderate-force contractions like distance running, the soleus is preferentially recruited due to it…
Muscle Strain Considerations
- Acute muscle strains are most commonly seen in bi-articular muscles that have a high proportion of fast twitch muscles fibers, usually with internally driven high levels of force like sprinting, or stretching movements like kicking. These instances produce high levels of force across the muscle. The most common muscles affected include rectus femoris, hamstrings, and gastrocne…
Muscle Strain Grading
- Historically, muscle strains have been graded as one, two or three, referring to mild, moderate or complete(5). There is, however, some ambiguity around this grading system. Alternative grading systems identify different parts of the muscle/tendon complex and more accurately reflect MRI findings of different level injuries(5). This also includes low-grade muscle injuries that do not ha…
Assessment
- The history as described above and the exact location of pain (both reported and on palpation) are key parts of an assessment. Physical assessment is relatively straightforward. The patient completes a double leg calf raise to determine the level of discomfort. Then perform another calf raise with the knees bent. Compare to the level of discomfort when performing with a bent knee …
Mechanism of Injury
- The potential underlying causes of soleus strain include (but are not limited to): 1. Training error – overtraining, rate of increase of training loads too high, introduction of too much hill work over too short a time, poorly designed training program – eg a hard running session after a long run 2. Kinetic chain dysfunctions – poor hip extension flexibility and associated poor gluteus maximu…
References
- Pflügers Archiv 348 (3): 247–55
- J Physiol. 1989 February; 409: 451–471
- Med Sci Sports Exerc [01 Oct 1993, 25(10):1163-1173
- Current Reviews in Musculoskeletal Medicine. June 2009, 2(2):74-77