The following are all great to add to your routine while you let your LCL heal:
- Spend plenty of time resting and icing the injury
- Wear a brace or compression wrap to prevent swelling
- Stay hydrated
- Eat a healthy, balanced diet to ensure your body has all the nutrients it needs for recovery
- Sit on the floor with your knees bent.
- Place a pillow between your knees.
- Put your hands slightly behind your hips for support.
- Squeeze the pillow by tightening the muscles on the inside of your thighs.
- Hold for 6 seconds, then rest for up to 10 seconds.
- Repeat 8 to 12 times.
How to treat an LCL sprain at home?
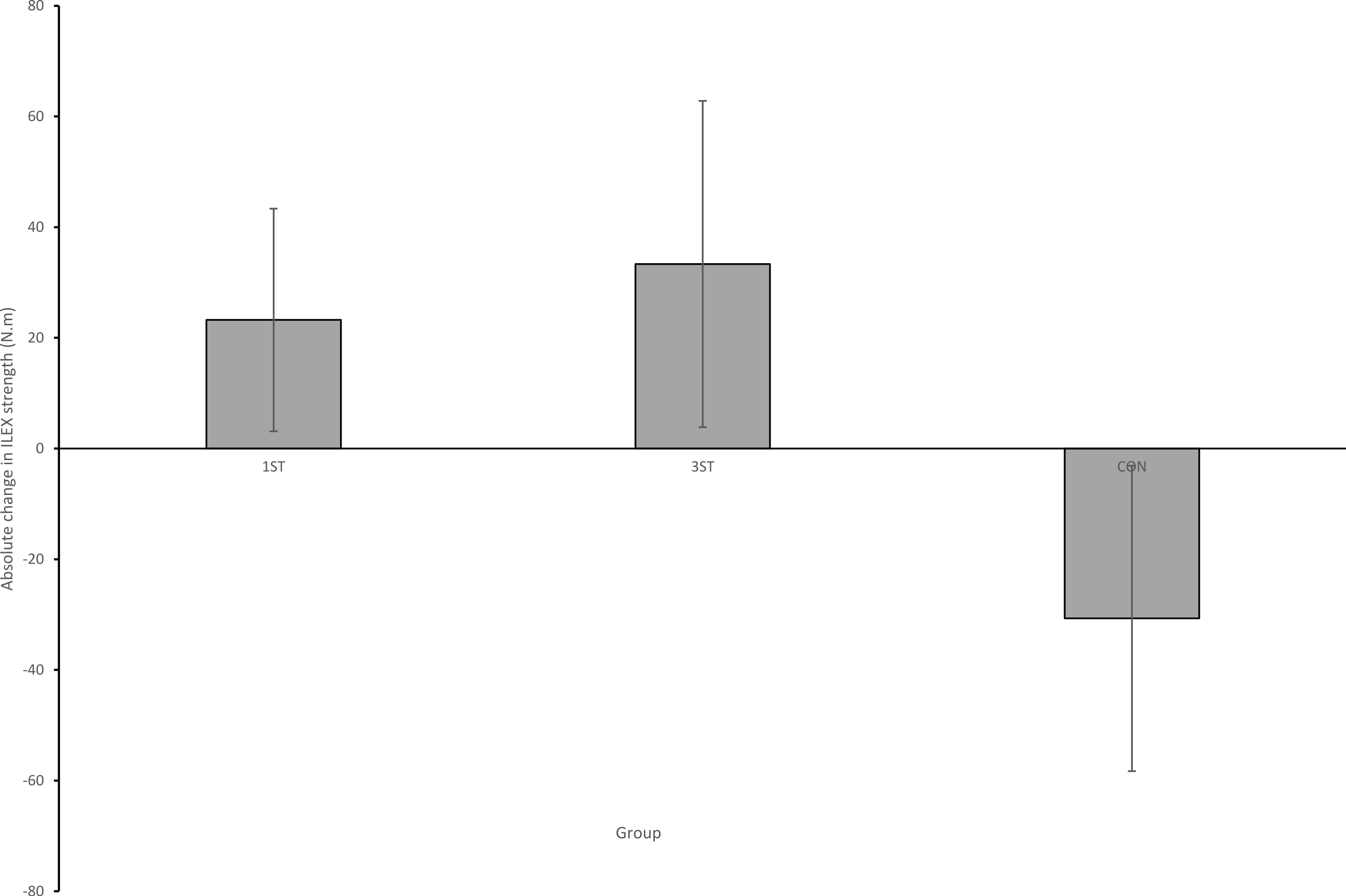
LCL PROTOCOL PHASE ONE Weeks 1-6 The patient will be in a post-op IROM brace with a 30° extension limit that will be maintained for at least 3 weeks and up to 6 weeks, at the physician’s discretion. The brace is to be worn at all times. The patient will be NWB until the extension limit is released. Keys during phase one: Protect the new graft
What are the symptoms of a torn LCL in the knee?
Jul 05, 2018 · Hip abduction and adduction exercises will help strengthen the hips and inner thigh muscles to better support the LCL. For hip abduction, start by lying on your side with your injured leg on top. Then, lift your leg as high as you can while making sure the toes are pointing forward. Hold for 5-10 seconds, then relax.
What are the symptoms of a Grade 1 LCL sprain?
How is a lateral collateral ligament (LCL) injury treated? Rest and protecting your knee. Ice or a cold pack. Wrapping your knee with an elastic bandage (compression). Propping up (elevating) your knee. Anti-inflammatory medicine.
What is an LCL injury?
Treatment The lateral collateral ligament does not heal well as a medial collateral ligament (MCL). For a minor tear, we suggest non-surgical treatment, which consists of rest, use of leg brace and icing. When the pain and swelling are gone, start exercises with a physical therapist to restore strength and range of motion of knee.

How long does a strained LCL take to heal?
LCL tears usually heal after three to 12 weeks, depending on severity. You have to take care of yourself, though. Use crutches, ice your knee and follow your healthcare provider's instructions.Aug 19, 2021
What is the fastest way to heal an LCL injury?
Most LCL injuries can be treated at home with:Rest and protecting your knee.Ice or a cold pack.Wrapping your knee with an elastic bandage (compression).Propping up (elevating) your knee.Anti-inflammatory medicine.
Can an LCL injury heal on its own?
No specific exercise can help a LCL heal. The ligament will heal on its own, and the main thing to do is to prevent re-injury to the ligament during its healing.
Is walking good for LCL injury?
You'll probably also do aerobic exercise, like walking, and wear a knee brace at first. If your LCL tore all the way through, you may need to have surgery to repair it.Jul 31, 2020
How do I strengthen my LCL knee?
You will need a pillow for this exercise.Sit on the floor with your knees bent.Place a pillow between your knees.Put your hands slightly behind your hips for support.Squeeze the pillow by tightening the muscles on the inside of your thighs.Hold for 6 seconds, then rest for up to 10 seconds.Repeat 8 to 12 times.
What are 4 symptoms of a LCL injury?
People with knee lateral collateral ligament (LCL) injuries often report a combination of the following symptoms:Pain along the outside of the knee. ... Tenderness. ... Swelling along the outside of the knee. ... Decreased range of motion. ... Knee catching or locking. ... Bruising. ... Trouble bearing weight. ... Foot numbness.
What does a LCL tear feel like?
The symptoms of an LCL injury are similar to other ligament injuries. You may experience pain and tenderness along the outside of the knee, along with swelling. Some people also describe a feeling of instability in their knee when walking, as if the knee may give out, lock or catch.
What foods strengthen knee ligaments?
Food for knee joints and ligaments that are considered anti-inflammatory, according to Harvard Health, include tomatoes, olive oil, green leafy vegetables, nuts like almonds and walnuts, fatty fish, and fruits such as berries and oranges. Olive oil, fatty fish and nuts all contain omega-3 fatty acids.Sep 23, 2019
How do you sleep with a LCL injury?
0:173:04Sleeping Positions with Pain + Injuries - Pt.2: Knees | Tim Keeley - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipSo if you can't sleep on your side because of knee pain. That's not comfortable. And you do want toMoreSo if you can't sleep on your side because of knee pain. That's not comfortable. And you do want to sleep on your back go back to the rules. Of shallow pillow there for your neck okay.
How do you rehab a knee ligament injury?
Quad setsSit with your affected leg straight and supported on the floor or a firm bed. Place a small, rolled-up towel under your knee. ... Tighten the thigh muscles of your affected leg by pressing the back of your knee down into the towel.Hold for about 6 seconds, then rest for up to 10 seconds.Repeat 8 to 12 times.
How to recover from a LCL injury?
When doing a hip flexion exercise, start by lying on your back. Bend the knee of your healthy leg and extend the injured leg out in front of you.
What sports are at risk for LCL sprain?
Many athletes are at risk of experiencing an LCL sprain, especially football players, basketball players, and baseball players, as well as those whose sports require a lot of quick direction changes.
What percentage of knee ligament injuries are lateral collateral ligament sprains?
In fact, they only account for approximately two percent of all knee ligament injuries.
What is a grade 1 sprain?
LCL sprains, like other ligament injuries, can be broken down into the following three categories: Grade 1: A grade 1 injury involves a small number of stretched ligament fibers, but no tearing. Grade 2: A grade 2 injury involves partial tearing of the ligament fibers.
How to abduct a hip?
For hip abduction, start by lying on your side with your injured leg on top. Then, lift your leg as high as you can while making sure the toes are pointing forward. Hold for 5-10 seconds, then relax. For hip adduction, flip over so your injured leg is on the bottom.
How to do quadriceps sets?
To do quadriceps sets correctly, extend your legs in front of you, flex your feet, and contract your quadriceps. Hold for 10 seconds, then relax.
How to tell if you have a LCL sprain?
Symptoms of an LCL sprain 1 The main symptoms of a lateral collateral ligament sprain (LCL sprain) is pain on the outside of the knee. 2 Pain can vary from being very mild to a complete rupture of the ligament. 3 You may have swelling over the outside of the joint.
How to heal lateral ligament injury?
Sports massage . Sports massage may help the healing of a lateral ligament injury when applied directly to the ligament in the form of cross friction massage. This may help to reduce scar tissue formation and re-align the new healing fibers with the ligament.
What does grade 2 mean in a sprain?
Grade 2. With a grade 2 LCL sprain, you will have significant tenderness on the outside of your knee, over the lateral ligament. You will likely have some swelling. A varus stress test will indicate pain and some laxity in your joint, although there is a definite endpoint indicating the ligament is still intact.
What is grade 3 lateral ligament sprain?
A grade 3 lateral ligament sprain is a complete tear of the ligament. Pain can vary and may be actually less than a grade 2 sprain. When stressing the knee there is significant joint laxity and you may have a very unstable knee.
What is the varus test?
The varus stress test is used to help diagnose injury to the lateral knee ligament by putting it under stress or tension. The therapist takes hold of the limb, ensuring the knee is slightly bent (approx 30 degrees). They stabilize the thigh whilst applying inward pressure on the lower leg.
What is the function of the lateral collateral ligament?
The ligament itself is a narrow strong cord of collagen fibres and its function is to provide stability to the outside of the knee. The LCL is most commonly injured in sports by a direct impact to ...
What is hinged knee brace?
A hinged knee brace will have solid metal supports at the sides to protect the knee from a lateral (sideways) movement which would stress the lateral knee ligament.
Why is LCL reconstruction important?
LCL/PLC reconstruction is important to avoid rotational instability of knee and subsequent cartilage damage. Depending on the extent of the damage, we are able to reattach the ligament with sutures or reconstruct it using donor tissue.
How to heal a knee injury?
When the pain and swelling are gone, start exercises with a physical therapist to restore strength and range of motion of knee. Recovery is seen depending upon grade of injury.
What is the pain in the outside of the knee?
Pain that can be mild or acute. Swelling and tenderness along the outside of the knee. A locking or catching in the joint when it is moved. Numbness or weakness in the foot may occur if the peroneal nerve, which is near the ligament is stretched during the injury or is pressed by swelling in surrounding tissues.
What is the function of the lateral collateral ligament?
The LCL is on the outside of the knee connecting the thighbone (femur) to the smaller bone in the lower leg (fibular). Its main function is to avoid varus stress across the knee (where the knee buckles outwards).
Can a doctor miss an ACL injury?
A careful eye is needed to diagnose a posterolateral and lateral injury; even an experienced physician can miss it, especially when it’s associated with an ACL injury, as the focus of the doctor and patient is on the ACL reconstruction.
When is the LCL torn?
The LCL is most commonly torn during sports activities or traumatic injuries (falls, etc.). The LCL is torn when the knee bends inwards excessively , and the LCL is stretched too far. LCL tears are graded similarly to other ligament tears on a scale of I to III:
What is grade 3 LCL tear?
Grade III LCL tears commonly occur alongside other injuries to the knee, most especially tears and sprains of the cruciate ligaments that connect the thigh bone (femur) to the shin bone (tibia). How Knee Ligament Injuries Are Diagnosed.
What is the LCL?
Stuart Hershman, MD. Updated on August 30, 2020. The lateral collateral ligament, or LCL, is one of the four major knee ligaments. The LCL connects the end of the thigh bone (the femur) to the top of the smaller shin bone (fibula), on the outside of the knee. The LCL helps to prevent excessive side-to-side movement of the knee joint.
What can I do to help my knee heal?
Activities including sports should be avoided until the ligament is healed. A brace can help to support the knee to prevent stress on the healing LCL. Anti-inflammatory drugs: Anti-inflammatory medications can help to control swelling and prevent inflammation.
What is the collateral ligament?
The lateral collateral ligament is one of the four major ligaments to provide stability to the knee joint. Injuries to the lateral collateral ligament are relatively uncommon compared to injuries to the other major knee ligaments. However, when the LCL is injured, people may have pain, swelling, and instability of the knee joint.
Symptoms of An Lcl Sprain
Anatomy
- The lateral collateral knee ligament or LCL for short connects the femur (thigh bone) to the top of the fibula (shin bone). The ligament itself is a narrow strong cord of collagen fibres and its function is to provide stability to the outside of the knee. The ligament is not connected to the lateral meniscus in the joint like the medial ligament (one the inside) does. Therefore, LCL sprain…
Causes
- The LCL is most commonly injured by a direct impact to the inner surface of the knee. For example, in a rugby or a football tackle. Force on the inside of the knee causes the joint to open on the outside, therefore stretching the lateral ligament. An LCL sprain is less common than a medial collateral ligament sprain.
Treatment
- Treatment consists of immediate first aid PRICE principles (Protection, Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation). This is followed by a full rehabilitation program.
Lcl Sprain Exercises & Rehabilitation
- Exercises for rehabilitation of lateral knee ligament sprains should include mobility, stretching, strengthening, proprioception, and eventually sports-specific exercises. Initially, isometric or static strengthening exercises are done. These progress to dynamic knee exercises involving movement. Proprioception exercises involve balance and coordin...
Surgery
- In grade 3 sprains, particularly when other structures such as an ACL tear or PCL tearare damaged, surgery may be needed. This is to prevent your knee from being unstable in the future. Your surgeon may suture (stitch) the torn ends of your LCL. Or they may reconstruct the ligament with a part of a tendon, e.g. a hamstring tendon.
References & Research
- LaPrade RF, Wentorf FA, Fritts H et al. A prospective magnetic resonance imaging study of the incidence of posterolateral and multiple ligament injuries in acute knee injuries presenting with a hem...