
In majority of the recovery can take 4 to 6 months or longer, depending on the size of the tear. Most activities can be resumed at 6 months, however the rotator cuff will heal for up to a year. Can rotator cuff heal on its own?
What is the average recovery time for rotator cuff repair?
Feb 16, 2022 · It is common for patients to require four to six months to recover fully from rotator cuff surgery. Complications may cause this schedule to be extended. Recovery time is frequently influenced by the following factors: The extent to which the rotator cuff has been torn. The extent to which the tear has occurred.
How long does it take to recover from rotator cuff surgery?
Shoulder impingement recovery time It may take as much as six months for a shoulder impingement to totally recover. Some severe impingements can take as much as a year to heal. Nevertheless, within two to four weeks, you ought to have the ability to resume your regular activities once again.
What is the recovery time for a rotator cuff injury?
Post-surgical care for impingement and rotator cuff tears are similar. General care recommendations include: Incisions must be kept dry for two or three days after surgery. Stitches are usually removed 7 - 10 days after surgery. Rehabilitation programs for impingement and rotators cuff surgery differ slightly.
When can you return to work after rotator cuff surgery?
Apr 11, 2022 · It is important to remember that oral anti-inflammatory medicines need to be taken for a time span of 8 weeks to fix the actual underlying cause of the disorder. A short term medication therapy may rid the patient of symptoms but if the cause is not treated properly the symptoms will recur.
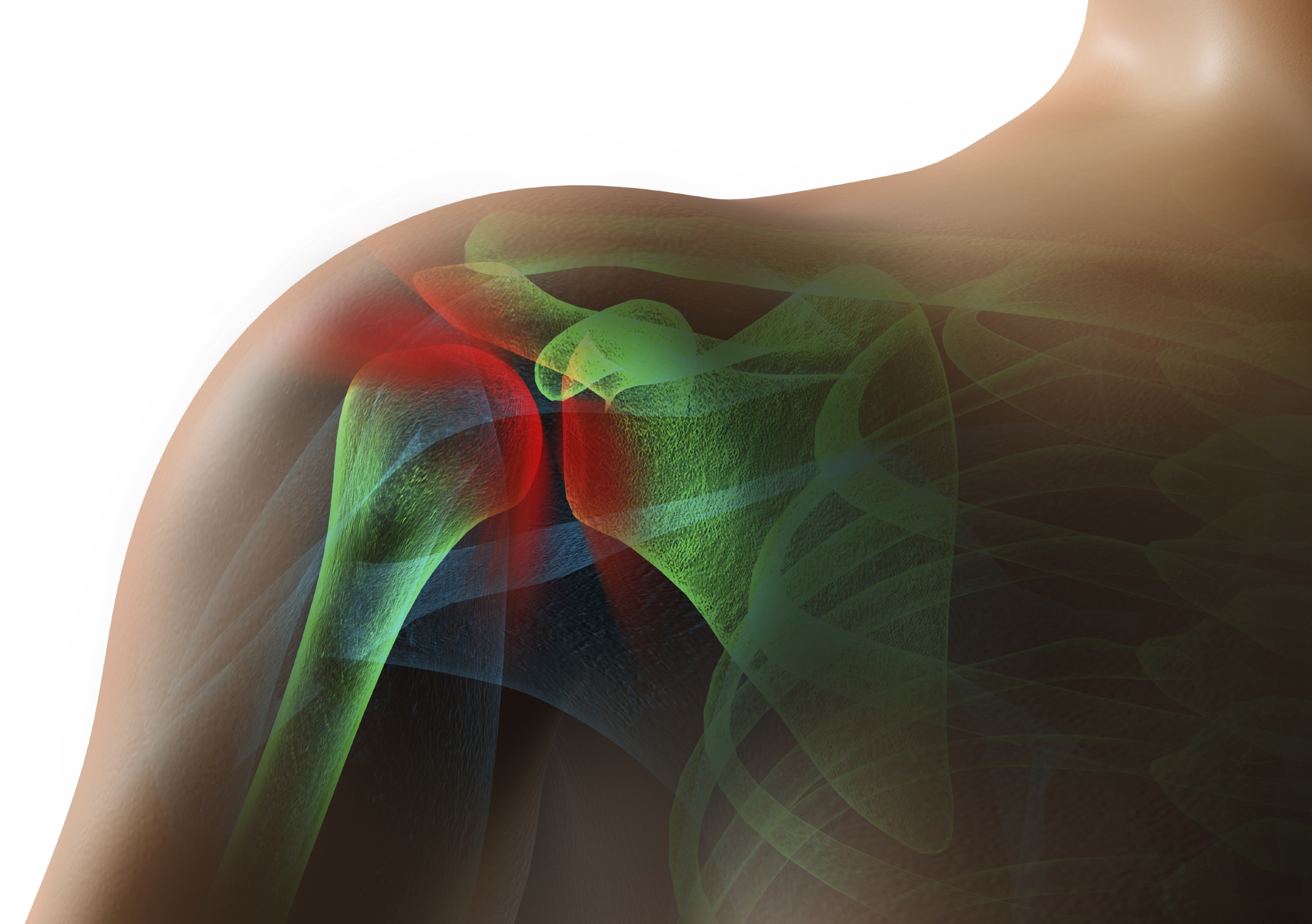
How long is shoulder impingement rehab?
Treatment for Shoulder Impingement The average recovery time for an impingement injury is about 6-8 weeks. Treatment may involve anti-inflammatory medications, stretching and strengthening exercises, and ice.Nov 8, 2018
How do you rehab a rotator cuff impingement?
Here are some exercises for shoulder impingement syndrome that may help relieve your symptoms:Scapula Squeeze. ... Scapula Push and Pull. ... Chest Stretch. ... Front Shoulder Stretch. ... Back Shoulder Stretch. ... Lying External Rotation. ... Internal Rotation with Resistance Band.
How long does a pinched rotator cuff take to heal?
Recovery is different for everyone, but it may take 3 to 4 months before your arm fully heals. During that time, you'll need to do daily exercises to rebuild your strength.Aug 21, 2020
What is the fastest way to heal a shoulder impingement?
Treatments for impingement syndrome include rest, ice, over-the-counter anti-inflammatory medications, steroid injections and physical therapy.Physical therapy is the most important treatment for shoulder impingement syndrome. ... Ice should be applied to the shoulder for 20 minutes once or twice a day.More items...•Jan 5, 2021
Can I still exercise with shoulder impingement?
Exercises to Help You Recover from Shoulder Impingement It's best to rest your shoulder, but you can do some light exercises to stretch the muscles in the arm, shoulder, and chest in conjunction with strengthening your rotator cuff.Dec 17, 2019
Should I stretch shoulder impingement?
Exercise addresses many of the modifiable risk factors that contribute to shoulder impingement. Stretching exercises increase the available space between the shoulder blade and humerus. This can alleviate compression of the rotator cuff, bursa, and biceps tendon.Aug 10, 2019
What should you not do with a shoulder impingement?
Avoid Reaching, Lifting, Pulling, or Pushing For about 4-6 weeks, avoid any movements with the affected shoulder that require exertion and effort. During your shoulder impingement treatment, use only your unaffected arm when opening doors, reaching for things and lifting items (such as bags).May 7, 2021
Can I do push ups with shoulder impingement?
Replace chest presses with push-ups. Chest presses target the pec muscles. But when you have an irritated shoulder, it may be difficult to perform. Luckily, the push-up works those chest muscles just as well.Aug 1, 2019
How can you tell the difference between a torn rotator cuff and impingement?
It differs from subacromial impingement syndrome where swelling due to repetitive or traumatic compression of structures causes pain and shoulder dysfunction, instead torn fibres of the muscle directly inhibit muscle function due to loss of structural integrity.Feb 27, 2019
Does impingement go away?
Symptoms may slowly go away over a period of weeks. It may take several months to fully recover. Drugs that reduce swelling, such as aspirin or ibuprofen. Avoiding any activities that cause pain, such as stretching or reaching past your comfort zone.
Can a chiropractor fix shoulder impingement?
Chiropractic of shoulder impingement is an effective option for your painful shoulder. Chiropractors can provide shoulder pain treatment including: Chiropractic adjustments to help with joint mobility and alignment. Soft tissue therapy to reduce tension in tight muscles and tendons.Mar 17, 2021
How do you sit with a shoulder impingement?
Follow these tips:When sitting, keep your head straight forward and don't let it tilt down. Sit with your knees slightly lower than your hips. ... When standing, keep your shoulders back and aligned. ... When sleeping, use pillows to minimize spinal curves.
How to treat rotator cuff impingement?
Treatment for impingement of rotator cuff varies from oral anti-inflammatory medications, physical therapy, lifestyle changes to prevent further damage and cortisone-type injections for more severe cases. 1. Medications. The most common treatment is oral anti-inflammatory medicines like aspirin, ibuprofen and naproxen.
What is used to treat small rotator cuff tears?
In a jointed X-ray, the shoulder joint is injected with a contrast dye and then a combination of X-ray, CT and MRI scans are used to get an enhanced picture of the region, helping doctors indemnity small rotator cuff tears.
What is the bursa of the rotator cuff?
The subacromial bursa is a fluid filled sac that lubricates the movement of rotator cuff and has pain sensors leading to pain in rotator cuff disorders.
Why does the rotator cuff hurt?
The impingement of rotator cuff occurs when the rotator cuff tendon and the subacromial bursa are pinched in the subacromial space, leading to inflammation and swelling. The impingement worsens when the arm is raised away from the body's side. Causes of impingement include: Old age and diseases like arthritis cause bone deformity which leads to ...
How to diagnose rotator cuff?
The doctor may order the following tests: 1 Starting with a physical examination, your doctor will observe tenderness on your shoulder area indicative of a Rotator cuff impingement. It is painful to raise arms overhead and the shoulder exhibits weakness when placed in particular positions. 2 An X-ray may also be taken to see if there are spurs on the bones of the shoulder area. 3 Ultrasound utilizes sound waves to create an image of the shoulder joint, which can show rotator cuff tear. 4 MRI of the shoulder can displays swelling and rotator cuff tear. 5 In a jointed X-ray, the shoulder joint is injected with a contrast dye and then a combination of X-ray, CT and MRI scans are used to get an enhanced picture of the region, helping doctors indemnity small rotator cuff tears.
What are the grades of impingement?
Impingement can be divided in three grades: Grade I : Inflammation of the bursa and tendon. Grade II: Thickening of the tendon and scarring of the bursa. Grade III: Rotator cuff starts to degenerate and tears are perceptible.
How to help a back pain?
2. Proper Exercise. Exercise along with medication is very effective in improving the condition. Stretching muscles daily when having warm water shower and moving thumb behind the back and up are useful for easing the pain.
What Is Rotator Cuff Impingement?
Your supraspinatus is one of four rotator cuff muscles responsible for elevating your arm away from your body and overhead. This important structure originates on your shoulder blade and travels through a small anatomical tunnel before attaching to your arm bone (humerus ).
Physical Therapy for Rotator Cuff Impingement
If you have significant and persistent shoulder pain, it's important to see your healthcare provider to get an accurate diagnosis. Some injuries, like a rotator cuff tear, may require more significant interventions such as surgery.
Surgical Treatment
In many instances, physical therapy and other conservative treatment is effective in addressing the symptoms caused by rotator cuff impingement. However, this is not always the case. In situations where PT is ineffective, surgery may be needed to address the underlying origins of your shoulder issue.
Summary
Rotator cuff impingement is a common cause of shoulder pain and impaired mobility of the arm and shoulder. Physical therapy can play an important role in easing your pain and restoring your ability to move freely.
A Word From Verywell
The pain and disability associated with rotator cuff impingement may be mild at first, but as symptoms progress, they can significantly impact your ability to go about your day. Because of this, it is important to seek treatment early on.
How long does it take for a rotator cuff to stabilize?
5. STABILIZE: Stabilize your shoulder. Within 3-14 days, you should begin rotator cuff strengthening exercises aimed at stabilizing your shoulder.
How deep is a rotator cuff tear?
In Grade 1 strains, the tear is only up to 3 millimeters deep [ 4 ]. In Grade 2 strains (or partial tears) the tear is 3-6 mm deep, or less than half the thickness of the involved tissue.
What muscles are involved in the rotator cuff?
Your rotator cuff is made up of the supraspinatus, infraspinatus, subscapularis, and teres minor muscles, which all run from your scapula to your humerus.
Why are there so many different classifications of rotator cuff tears?
There are many different classifications used for rotator cuff tears simply because of the complex nature of the area. There are 4 muscles involved and any one (or a combo of several) can be affected, all to different severities.
How to get a scapula out of your rib cage?
Widen your rib cage as you protract the scapulae – your body should move slightly toward the wall. Hold for 1-2 seconds. Retract the scapulae, moving slightly away from the wall and holding.
How to treat a doggie shoulder?
To treat the inflammation that is no doubt dogging your injured shoulder, apply ice for the first 24 to 72 hours after the pain develops . After that, only ice if excessive pain is provoked, but continue to run cold water over the painful area in the shower. (Yowza – I know – but trust me.)
How to do a drop arm test?
The Drop Arm Test is done by abducting your shoulder to reach the arm up. Start to lower your arm slowly, all the way to the side of your body.
What happens when you get caught in the rotator cuff?
As the tendons get caught, a number of things can occur; most commonly, the rotator cuff insertion where the supraspinatus attaches is squashed and rubbed on other structures, causing inflammation of the tendon (tendonitis) and pain. If the tendonitis is not addressed, the tendon becomes weaker over time and the person develops a ‘tendinopathy’ ...
What happens if you don't address rotator cuff tendonitis?
If the tendonitis is not addressed, the tendon becomes weaker and the function of the rotator cuff is compromised, leading to the cycle of impingement.
Why are my rotator cuff muscles sore?
Because the rotator cuff tendons are sore, inflamed and weakened, they don’t perform their stabilisation and movement assisting jobs. Once they start becoming weak, the continuation of conventional exercises, like lateral raises, and shoulder and bench presses, will result in the tendons getting increasingly caught.
Why is the rotator cuff underdeveloped?
This imbalance is increased with weak scapular stabilisers and tight rotator cuff muscles, mostly because muscles like serratus and lower trapezius are underdeveloped due to a lack of functional and stability exercises and an overuse of power and pressing exercises.
Why does my rotator cuff tear?
If the tendonitis is not addressed, the tendon becomes weaker and the function of the rotator cuff is compromised, leading to the cycle of impingement. In severe chronic and long term cases, the tendon becomes so weak it tears. The most common cause of impingement is having an ‘unbalanced’ shoulder and performing repetitive heavy pressing exercises ...
What muscles move the arm bone around?
The power muscles (deltoid, lats, pecs), meanwhile, move the arm bone around. Impingement can occur when the rotator cuff tendons or bursae get trapped in the ‘sub-acromial space’ which is the gap between the roof of the shoulder (acromion) and the ball of the humerus (glenoid head) during the arm movement, mostly abduction above 90 degrees.
What muscles move the shoulder blade?
The shoulder joint moves with two muscle systems, a postural system and a power system. The postural muscles control the shoulder blade movement and stability (i.e. serratus anterior, trapezius) and the shoulder joint rotation movement and stability (the rotator cuff). The power muscles (deltoid, lats, pecs), meanwhile, move the arm bone around.
How long does it take for rotator cuff to heal?
If your symptoms don’t go away after 6 months, your doctor could suggest surgery. You may also need it if one of your tendons is torn and can’t heal on its own. The most common surgery to fix a rotator cuff impingement is called a subacromial decompression (SAD).
What is the rotator cuff?
It affects the muscles and tendons between your arm bone and the top of your shoulder. You use this group of muscles and tendons , called the rotator cuff, to move and lift your arms. An impingement happens when one of these tendons is injured, causing it to swell and get pinched by the bony top of your shoulder joint.
What is grade 2 rotator cuff?
Grade 2: tendinopathy, or weakened tendons in the shoulder. Grade 3: tears in the rotator cuff or changes in the shoulder bone, such as the growth of bony spurs called osteophytes. Rotator cuff impingement is most common in older adults and athletes, but 20% of all people will get it at some point in their lives.
What grade of tendon fracture is caused by a rotator cuff tear?
Doctors sort these injuries into three grades based on your symptoms and how much damage the impingement causes: Grade 3: tears in the rotator cuff or changes in the shoulder bone, such as the growth of bony spurs called osteophytes.
What are the different types of shoulder impingement?
Doctors sort these injuries into three grades based on your symptoms and how much damage the impingement causes: 1 Grade 1: swelling and inflammation 2 Grade 2: tendinopathy, or weakened tendons in the shoulder 3 Grade 3: tears in the rotator cuff or changes in the shoulder bone, such as the growth of bony spurs called osteophytes
How do you know if you have a rotator cuff?
Rotator Cuff Impingement Symptoms. If you have a rotator cuff impingement, you’ll notice pain in your shoulder. It will be worse when you reach your arms behind your back, raise them overhead, or make twisting motions, such as trying to put on a coat. Some people wake up at night because of the pain.
What to do when your shoulder hurts?
You’ll need to stop all physical activity that puts stress on your shoulder or causes you pain. This may include things you do at your job. Pain relievers. Over-the-counter NSAIDs (nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) like aspirin, ibuprofen, or naproxen can ease your pain.
What is the function of the rotator cuff?
Understanding the functional anatomy of the rotator cuff assists in understanding its disorders. The rotator cuff is the dynamic stabilizer of the glenohumeral joint. The static stabilizers are the capsule and the labrum complex, including the glenohumeral ligaments. Although the rotator cuff muscles generate torque, they also depress the humeral head. The deltoid abducts the shoulder. Without an intact rotator cuff, particularly during the first 60 degrees of humeral elevation, the unopposed deltoid would cause cephalad migration of the humeral head, with resulting subacromial impingement of the rotator cuff. 1 In patients with large rotator cuff tears, the humeral head is poorly depressed and can migrate cephalad during active elevation of the arm. This migration is sometimes evident even on plain radiographs. 2
Why does the rotator cuff impinge?
Impingement may occur as a result of loss of competency of the rotator cuff. Pain from any cause, such as overuse or injury, may lead to disuse or weakness of the cuff. The weakness results in cephalad migration of the humeral head due to loss of depressors.
What are the four muscles of the rotator cuff?
The rotator cuff comprises four muscles—the subscapularis, the supraspinatus, the infraspinatus and the teres minor —and their musculotendinous attachments. The subscapularis muscle is innervated by the subscapular nerve and originates on the scapula. It inserts on the lesser tuberosity of the humerus. The supraspinatus and infraspinatus are both innervated by the suprascapular nerve, originate in the scapula and insert on the greater tuberosity. The teres minor is innervated by the axillary nerve, originates on the scapula and inserts on the greater tuberosity. The subacromial space lies underneath the acromion, the coracoid process, the acromioclavicular joint and the coracoacromial ligament. A bursa in the subacromial space provides lubrication for the rotator cuff ( Figure 1).
What are the symptoms of shoulder pain?
Pain is exacerbated by overhead or above-the-shoulder activities. A frequent complaint is night pain, often disturbing sleep, particularly when the patient lies on the affected shoulder.
Can acromioclavicular ligaments cause impingement?
The coracoacromial ligament can also calcify, usually secondary to trauma, and cause impingement. In most cases, acromioclavicular joint arthritis is the culprit, resulting from previous trauma (separations) or, most often, nontraumatic osteoarthritis.
Can a rotator cuff tear be repaired?
Not all cuff tears diagnosed clinically, or by arthography or MRI require surgical repair. A rotator cuff tear is not, in itself, an indication for surgery. 15, 16 In fact, survey studies using MRI have shown a high incidence of unsuspected full or partial tears of the rotator cuff in asymptomatic adults. 17, 18 Most older patients with impingement and rotator cuff tears actually do well without surgery. However, surgery might be considered in a patient who has failed to improve after six months of conservative treatment or in a patient less than 60 years of age with a debilitating tear that impairs function.
